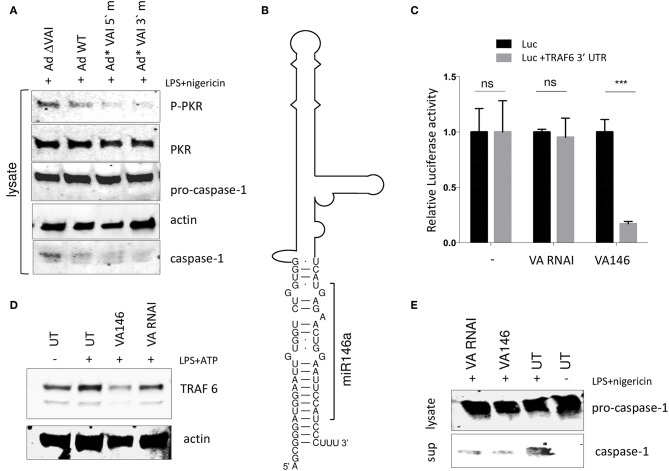
Figure 7.
A VA RNAI terminal stem chimera expressing miR-146 reduces TRAF6 accumulation retains the ability to inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome. (A) Western Blot showing that replication competent Ad5 viruses with mutations in either the VA RNAI 5′or 3′seed sequences (Ad*VAI 5′m and Ad*VAI 3′m) were as efficient as Ad WT in preventing phosphorylation of PKR and blocking the release of caspase-1. (B) Schematic diagram showing the sequence of the Ad5 VA RNAI/miR-146 chimera. (C) HEK293 cells co-transfected with in vitro transcribed wild type VA RNAI or VA146 and luciferase reporters containing or lacking the miR-146 binding site from the TRAF6 mRNA demonstrates a miR146 dependent-repression of luciferase activity. (D) Western blot analysis showing that transfection of in vitro transcribed VA146 down-regulates endogenous TRAF-6 protein expression in NLRP3 inflammasome activated (LPS + ATP treated) THP-1 cells. (E) Western blot analysis showing that in vitro transcribed VAI146 and wild type VA RNAI inhibit IL-1ß release in NLRP3 inflammasome activated (LPS + ATP treated) THP-1 cell to the same degree. The quantitated data represent the mean ± SE from three independent experiments. Results are depicted as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by Unpaired t-test ***p < 0.001; n.s. not significant.