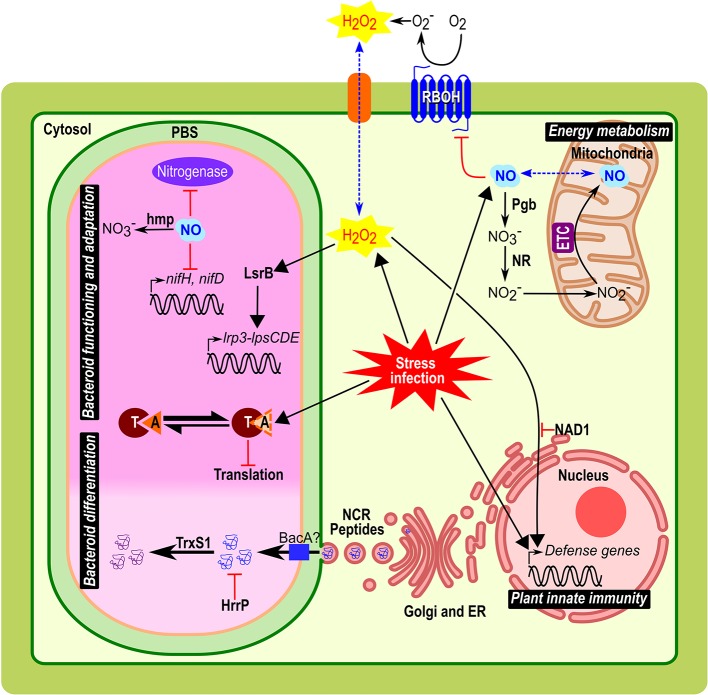
Figure 1.
Implication and connection of ROS, NO, NCR peptides, and TA modules in symbiosomes from Medicago root nodules. Biological role of these compounds during bacteroid differentiation, nodule functioning and adaptation, plant innate immunity, and energy metabolism are represented. Plant host cells infected by bacteria/bacteroid, implied various stress responses such as oxidative/nitrosative stress, acidic pH, microoxia, and exposure to NCRs. In the symbiosome, the clear part corresponds to the infection zone and the dark pink to the fixation zone with bacteria differentiated in bacteroid. Black arrows indicate metabolism reaction or downstream signal transduction pathways; red arrows indicate regulation mechanism (activation with arrowhead or repression with bar-headed lines). Blue dotted arrow indicates a diffusion through the membrane. Abbreviations: PBS, peribacteroid space; NR, nitrate reductase; Pgb, Phytoglobin; RBOH, respiratory burst oxidase homologs; O2 −, superoxide radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; ETC, electron transfer chain; NO, nitric oxide; ER; endoplasmic reticulum; NCR peptides, nodule-specific cysteine-rich peptides; Hmp, flavohemoglobin; NAD1, Nodules with Activated Defence 1; TrxS1, Thioredoxine S1; HrrP, Host-range restriction peptidase; LsrB, LysR transcription factor; T, toxin; A, antitoxin.