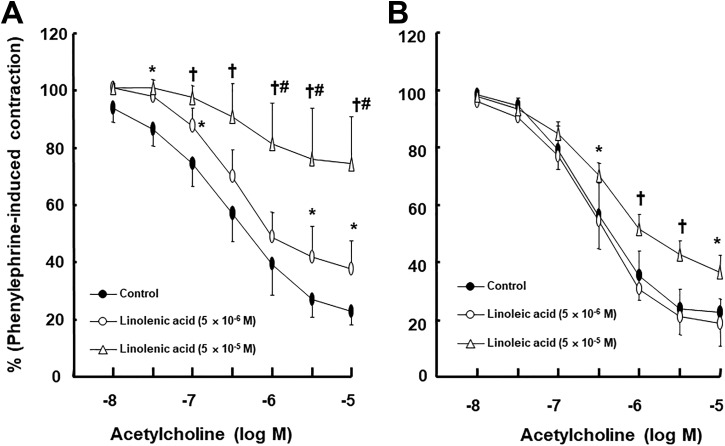
Figure 1.
Effect of linolenic acid (A) and linoleic acid (B) on acetylcholine-induced relaxation in isolated endothelium-intact rat aortae. Data (A: control, 5 × 10−6 and 5 × 10−5 M linolenic acid: N = 10, 5, and 6, respectively; B: control, 5 × 10−6 and 5 × 10−5 M linoleic acid: N = 6, 5, and 5, respectively) are shown as mean ± standard deviation and expressed as the percentage of maximal contraction induced by phenylephrine. N indicates the number of rats in which thoracic aortae were obtained. *P < .05 and † P < .001 versus control. # P < .001 versus 5 × 10− 6 M linolenic acid.