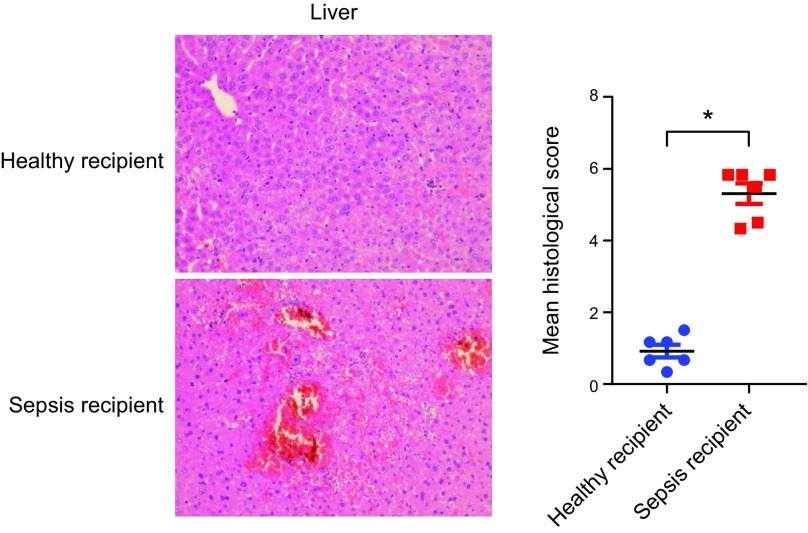
Figure 4.
Sepsis-linked gut dysbiosis promoted polymicrobial sepsis-induced liver injury in mice. Mice were intragastrically administered antibiotics once daily for 5 d to deplete the gut microbiota. Then, mice were randomly distributed into 2 groups (healthy and sepsis recipient groups). The stool samples from the participants of the 2 groups (healthy individuals and patients with sepsis) were collected and resuspended in PBS at 0.125 g/ml. Then, 0.15 ml was orally inoculated to mice of both groups. After 3 d, the mice were subjected to severe CLP and euthanized 8 h after CLP treatment. Hepatic hematoxylin and eosin staining and the histologic score, n = 6. *P < 0.05.