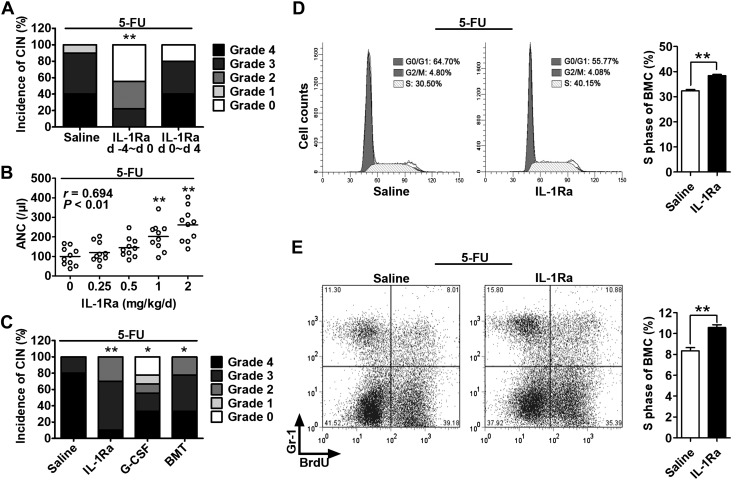
Figure 2.
rhIL-1Ra alleviated neutropenia by protecting hematopoietic cells from 5-FU cytotoxicity. A–C) Mice received 5-FU (100 mg/kg) at d 0. The ANC per microliter at d 7 after 5-FU (nadir point) was graded according to the Clinical Criteria for Adverse Events. CIN severity was rated as follows: 0, ≥600; 1, 450–600; 2, 300–450; 3, 150–300; 4, <150. A) Mice were treated with saline or rhIL-1Ra (2 mg/kg) daily for 5 d either before (−4 to 0 d) or after (0–4 d) 5-FU administration. CIN incidence and severity were plotted. **P < 0.01 (n = 9–10). B) The CT26 tumor-bearing mice received rhIL-1Ra before 5-FU. The correlation between ANC and rhIL-1Ra dose was plotted. Pearson correlation coefficient r = 0.694; P < 0.01 (n = 9–10). C) The CT26 tumor-bearing mice were treated with rhIL-1Ra (2 mg/kg/d; −4 to 0 d), recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) (1 μg/d; 3–7 d), or BM transplantation (BMT) (4 × 106 BMCs; d 1). All mice received 5-FU at d 0. CIN incidence and severity were plotted. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (n = 9–10). D) BMC cell cycle analysis at d 7 after 5-FU. The cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after propidium iodide staining. The bar graph on the right indicates the mean percentage ± sem of the BMCs in S phase in the saline or rhIL-1Ra pretreatment group. **P < 0.01 (n = 5). E) BrdU incorporation assay for newly BM-produced granulocytes. After in vivo BrdU labeling for 3 h on d 7 after 5-FU treatment, the BrdU-labeled BMCs were stained with Gr-1 antibody and analyzed by flow cytometry. The bar graph on the right indicates the mean percentage ± sem of BrdU+Gr-1+ cells in mouse BM derived from the saline or rhIL-1Ra pretreatment group. **P < 0.01 (n = 6).