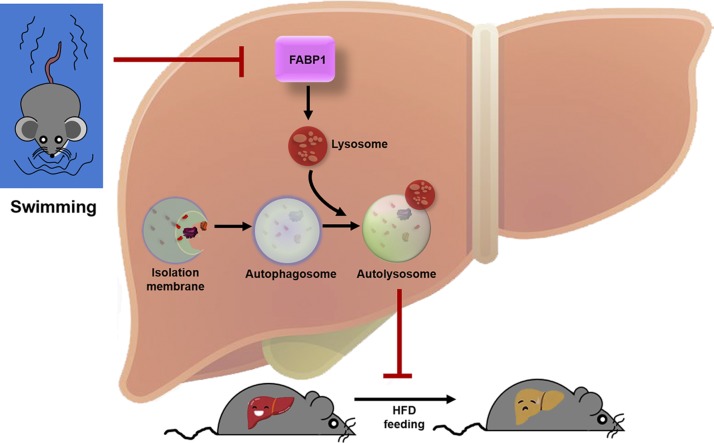
Figure 9.
Schematic model of exercise prevents HFD-induced hepatic steatosis: regulation of autophagy-lysosomal machinery via inhibiting the FABP1 pathway. HFD exposure stimulates an increase in FABP1 in the lysosome, and FABP1 triggers lysosomal dysfunction and subsequently leads to autophagic flux impairment and hepatic steatosis. Moreover, FABP1 inhibition–mediated replenishment of the autophagy-lysosomal machinery represents a novel endogenous mechanism whereby long-term exercise improves lipid homeostasis and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in NAFLD.