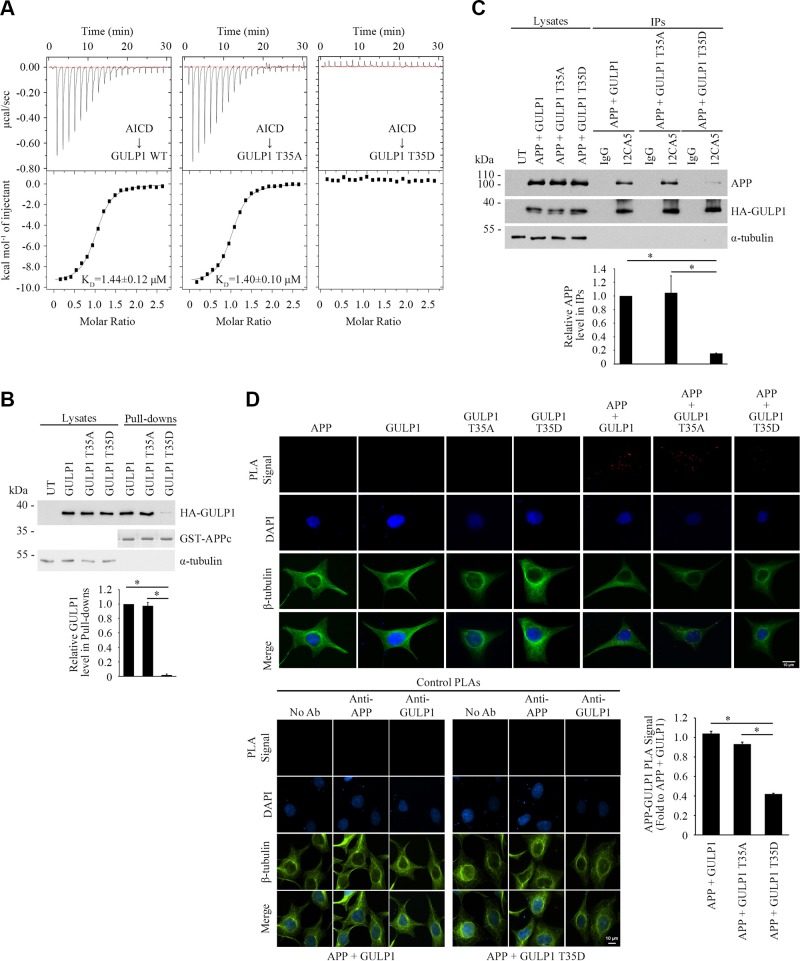
Figure 2.
GULP1 T35 phosphomimetic mutation reduces GULP1-APP interaction. A) ITC-based measurements of the binding between AICD peptide and PTB domains from WT GULP1 (left), GULP1 T35A (middle), or GULP1 T35D (right). B) Bacterially expressed GST-APPc was used as bait for GST pull-down assay from GULP1, GULP1 T35A, or GULP1 T35D–transfected cell lysate. GULP1 was detected by a rat anti-GULP1. Middle panel: Coomassie Blue staining of GST-APPc bait used. C) Coimmunoprecipitation was performed from CHO cells transfected with APP + GULP1, APP + GULP1 T35A, or APP + GULP1 T35D using a mouse anti-HA antibody 12CA5 to the N-terminal HA-tag of GULP1. APP and GULP1 in the immunoprecipitates (IPs) were detected by a rabbit anti-APP and a rat anti-GULP1, respectively. Data for graphs (B, C) were obtained from 3 independent experiments (n = 3). Results are means ± sd. *P < 0.001. D) GULP1 T35D reduces GULP1-APP interaction in PLA. HEK293 cells were transfected with APP + GULP1, APP + GULP1 T35A, or APP + GULP1 T35D. Fewer PLA signals were observed in APP + GULP1 T35D cotransfected cells. No signal was detected in APP, GULP1, GULP1 T35A, or GULP1 T35D singly transfected cells. β-Tubulin and DAPI were used as morphology and nucleus markers, respectively. Representative images are shown (upper left panel). Bar chart shows relative PLA signal (fold to APP + GULP1). Data were obtained from at least 60 cells per transfection and the experiments were repeated 3 times. Error bars are sem. *P < 0.001. No-antibody (No Ab), anti-APP, and anti-GULP1 control PLAs were performed for APP + GULP1 and APP + GULP1 T35D transfected cells (lower panel).