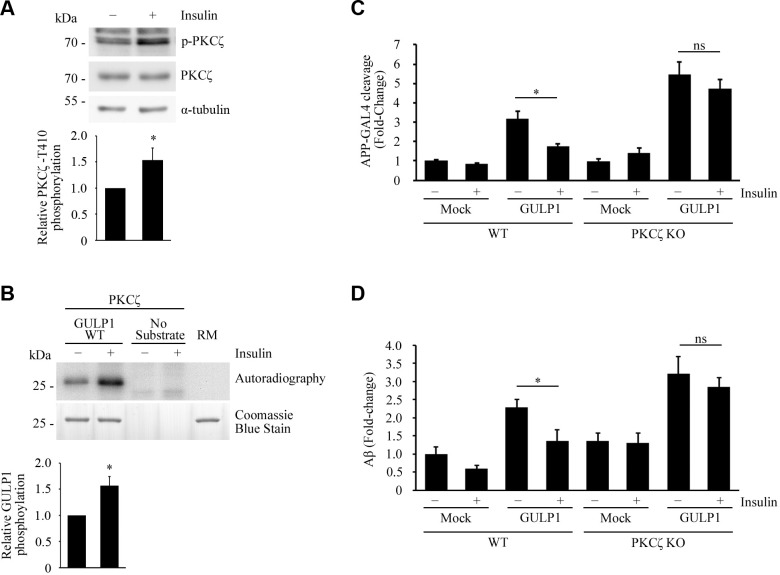
Figure 4.
Insulin stimulates PKCζ and suppresses GULP1-mediated APP processing. A) Serum-starved HEK293 cells were incubated in culture medium containing 0 (−) or 100 nM (+) insulin. T410-phospho-PKCζ, total PKCζ, and α-tubulin in cell lysates were detected by a rabbit anti-PKCζ phospho-T410, rabbit anti-PKCζ, and anti–α-tubulin DM1A antibody, respectively. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of PKCζ T410. Bar chart shows relative PKCζ T410 phosphorylation (n = 3). *P < 0.001. B) Bacterially expressed GST-GULP126–43 was incubated with PKCζ immunoprecipitated from untreated (−) or 100 nM insulin-treated (+) transfected cell lysate together with (γ-[32P])-ATP for 5 min at 30°C. RM is the reaction mix only without kinase. Upper panel: autoradiograph; lower panel: Coomassie Blue staining. Insulin potentiates GULP1 T35 phosphorylation by PKCζ. Bar chart shows relative GULP1 phosphorylation (n = 3). *P < 0.001. C) WT or PKCζ knockout (KO) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with APP-GAL4, pFR-Luc, and phRL-TK together with the indicated constructs. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 4 h and then treated with either 0 (−) or 100 nM (+) insulin for 12 h. Insulin reduces the effect of GULP1-mediated APP-GAL4 cleavage in WT cells but not in PKCζ KO cells. Ns, not significant (n = 5). *P < 0.001. D) WT or PKCζ KO HEK293 cells were cotransfected with APP and the indicated constructs. Twenty-four hours post-transfection, cells were serum starved for 4 h and then treated with either 0 (−) or 100 nM (+) of insulin for 17 h. The cells were replenished with fresh medium containing 0 (−) or 100 nM (+) of insulin for 7 h and the level of secreted Aβ40 was assayed. Insulin reduces the effect of GULP1-mediated Aβ40 production in WT cells but not in PKCζ KO cells. Ns, not significant (n = 5). *P < 0.001.