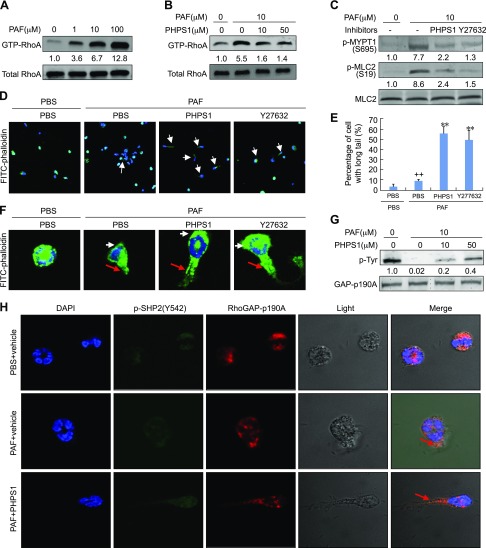
Figure 4.
Participation of RhoA/ROCK signaling in SHP2-mediated eosinophil migration. A) RhoA activation by PAF. Rat eosinophils were treated with the indicated concentrations of PAF for 5 min. Cells were then harvested for RhoA pull-down assays and Western blotting. GTP-RhoA was normalized to total RhoA. B, C) Inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling by PHPS1. Rat eosinophils were treated with 10 μM PAF for 5 min in the presence or absence of 50 μM or indicated concentrations of PHPS1 or 10 μM Y27632. Cells were then harvested for RhoA pull-down assays and Western blotting. Phosphorylated protein was normalized to total protein. D–F, H) Eosinophil chemotaxis toward PAF. Rat eosinophils were plated into gelatin-coated chamber slides and pretreated with 50 μm PHPS1 or 10 μm Y27632 for 30 min. The micropipette loaded with 100 μM PAF was then screwed in the plate to allow the chemotaxis of eosinophils for 30 s. Cells were then fixed and subjected to immunostaining of FITC-labeled phalloidin (D, F) and quantification (E) of p-Y542-SHP2, RhoGAP-p190A, and DAPI (H). F) Representative cells from D. White arrow, membrane protrusions at the front of eosinophil; red arrow, retracting fiber at the rear of eosinophil. G) Rat eosinophils were treated with 0 or 10 μM PAF in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of PHPS1 for 5 min and cells were then harvested for immunoprecipitation by a RhoGAP-p190A antibody. Western blotting was performed to detect the levels of phosphotyrosine and RhoGAPp190A in the immunoprecipitated complex. Data are presented as means ± sd (n = 3). ++P < 0.01 vs. PBS and PBS; **P < 0.01 vs. PAF and PBS.