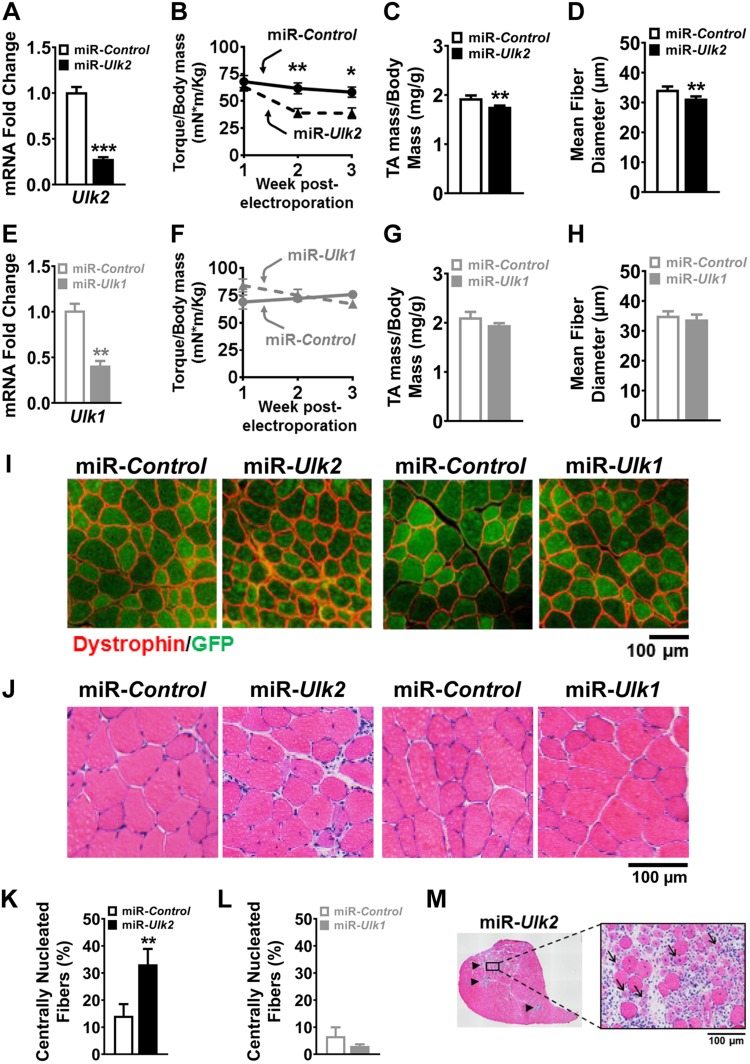
Figure 5.
ULK2 is required for maintenance of skeletal muscle force, mass, and integrity. Data were obtained from control and ULK-deficient TA muscles 4 wk after electroporation. A) Relative Ulk2 mRNA in control and ULK2-deficient muscles (n = 5–6). B) Weekly monitoring of maximal isometric torque in ankle dorsiflexors in mice with unilateral TA deficiency of ULK2 (n = 5). C) Wet muscle mass normalized to body mass in control and ULK2-deficient muscles (n = 5). D) Mean muscle fiber diameter as previously indicated in C (n = 6). E) Relative Ulk1 mRNA in control and ULK1-deficient muscles (n = 5–6). F) Weekly monitoring of maximal isometric torque in ankle dorsiflexors in mice with unilateral TA deficiency of ULK1 (n = 6). G) Wet muscle mass normalized to body mass in control and ULK1-deficient muscles (n = 6). H) Mean muscle fiber diameter as previously indicated in G (n = 6). I) Representative images of myofibers following immunofluorescence staining for dystrophin and GFP in control and either ULK2- or ULK1-deficient muscles. J) Representative H&E images denoting centrally nucleated fibers in ULK2-deficient muscle. K) Quantification of centrally nucleated fibers in control and ULK2-deficient muscles (n = 6). L) Quantification of centrally nucleated fibers in control and ULK1-deficient muscles (n = 6). M) Representative H&E images of an entire cross section of ULK2-deficient muscle depicting areas of myofiber degeneration and regeneration (black arrow heads, left) and an enlarged area denoting several abnormally small, centrally nucleated, degenerating fibers surrounded by infiltrating cells (black arrows, right). Data are means ± sem. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.