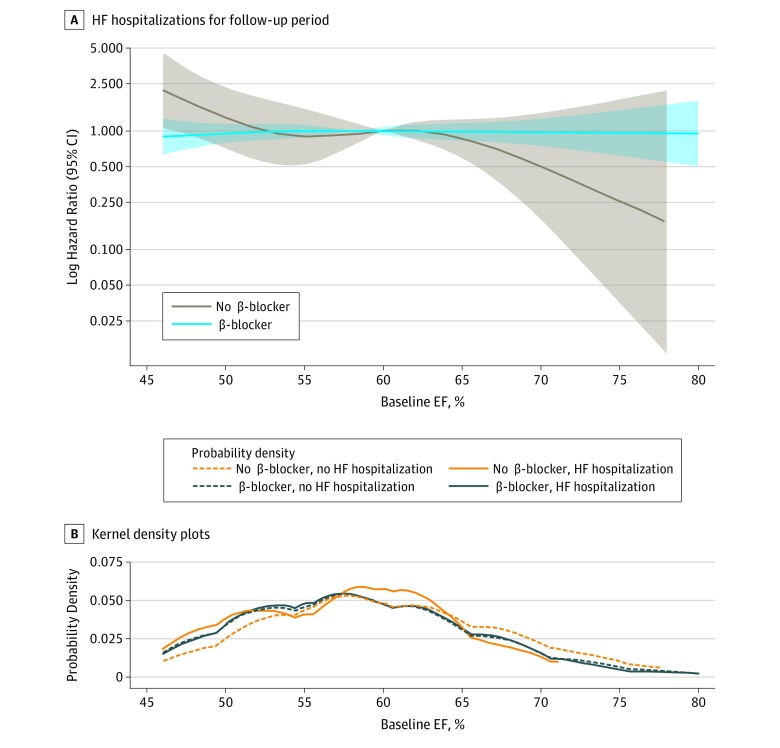
Figure 3. Restricted Cubic Splines and Kernel Density Plot Relating Hazard Ratios for Heart Failure (HF) Hospitalization and Ejection Fraction (EF).
A, Hazard ratios for incident HF hospitalizations for the follow-up period, according to baseline EF using restricted cubic spline models, adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, treatment assignment, prior myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and hypertension. The shaded areas represent the 95% CIs. The logarithmic scale on the y-axis indicates hazard ratios for HF hospitalization, where values greater than 1 indicate greater rate of HF hospitalizations and values less than 1 indicate fewer HF hospitalizations are related to an EF on the x-axis. The models were expressed relative to the median EF. Four knots were specified using the Harrell method and were not prespecified.24 Knots were 43.0%, 53.0%, 59.0%, and 71.7% for β-blocker and 47.0%, 57.0%, 62.0%, and 72.0% for no β-blocker. The plots were truncated at 0.5% and 99.5% of baseline EF. B, Kernel density plots demonstrating the distribution of baseline EFs.