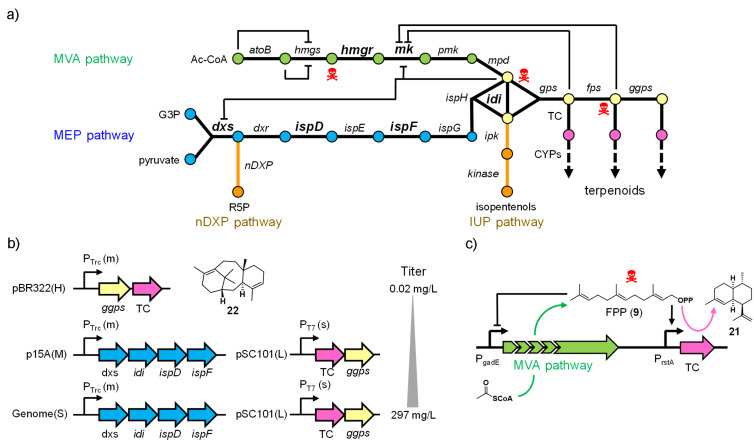
Figure 11.
Engineering of terpenoid pathways. a) Metabolic network of terpenoid biosynthesis. Toxic intermediates are labeled with skull signs and known enzyme inhibition by intermediates is indicated. Bottleneck enzymes that have been subjected to optimization/engineering are highlighted in bold. Two novel pathways, nDXP and IUP, provide alternative entry points to terpenoid biosynthesis. b) Balancing gene expression for taxadiene (22) production in E. coli. The copy number of the constructs are labeled with upper case letters: H: high, M: medium, L: low, and S: single copy. The relative strength of the promoter is labeled with lower case letters: s: strong and m: medium. This tuning led to 15,000-fold increase in taxatidene titer. c) Two FPP (9)-responsive promoters were implemented to dynamically control the expression of MVA pathway genes and the terpene cyclase gene in order to prevent the accumulation of toxic FPP (9).