Figure 1.
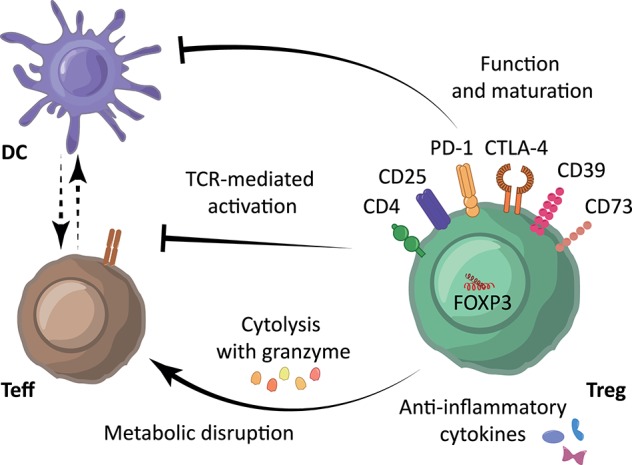
Immunosuppressive mechanisms underlying Treg-mediated immune suppression. Treg are characterized by expression of the cell surface markers CD4+, CD25high and CD127low/−, and transcription factor FOXP3. Treg modulate the immune system using their suppressive molecules PD-1, CTLA-4, CD39, and various surface receptors through inhibition of dendritic cell (DC) function and maturation, through the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10, TGF-β and IL-35, and/or through direct inhibition of Teff via induction of cytolysis using granzyme and metabolic disruption. Moreover, Treg can reduce Teff activation by limiting TCR-ligand binding.
