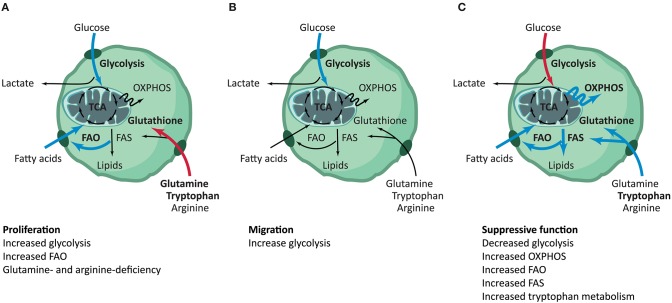
Figure 3.
Summary of metabolic pathways involved in distinct Treg functionalities. Treg have distinct metabolic phenotypes throughout their different phases, although many pathways remain to be elucidated. (A) During proliferation, Treg have increased glycolysis and FAO. Deficiency of glutamine and tryptophan steers T cells toward Treg differentiation (10–31). (B) To support the increased need for energy during migration, Treg increase their glycolytic flux. Metabolic shifts in other pathways have not been described for Treg migration (15, 16, 33–39). (C) Treg show decreased glycolysis and increased OXPHOS, FAO, FAS and tryptophan metabolism during their phase of suppressive function. No relevance for the TCA cycle has been reported (6, 10, 14–17, 21, 25, 26, 29, 31, 40–53). The blue and red arrows are indicative for increased or decreased activity of the specific pathway in the functional phenotype of Treg, respectively. FAO, fatty acid oxidation; FAS, fatty acid synthesis; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation.