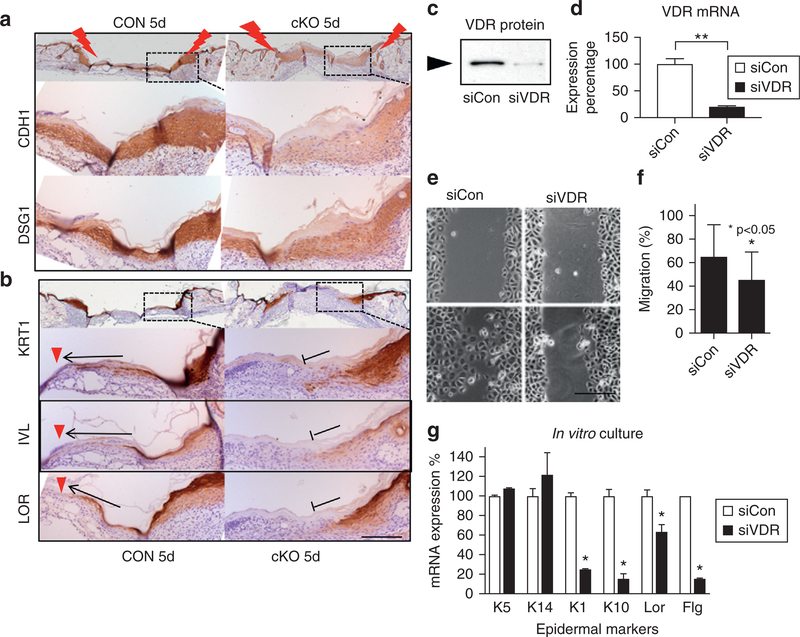
Figure 5. VDR ablation prevents differentiation of progeny.
At late stage of wound healing (5 days after wounding), epithelial markers (a) and differentiation markers (b) are shown at the edge of CON and cKO wounds (brown with blue counterstaining). Arrows and red triangles show extension of differentiated cells in CON, and stop signs show their defects in cKO. Scale bar = 100 μm. (c–g) VDR was silenced in cultured keratinocytes (siVDR). Blocking efficiency of VDR by Western (c) and quantitative PCR (d) (**P < 0.01) is shown. (e) Images for cell migration by the scratch assay (scale bar = 25 μm) and (f) their quantitation (*P < 0.05, n = 12). (g) mRNA expression of differentiation markers (quantitative PCR, 1.2 mM calcium, 3-day culture) (n = 3, P < 0.05). cKO, conditional knockout CON, control; si, small interfering; VDR, vitamin D receptor.