Figure 5 -. Y1 receptor internalization induced by capsaicin, NMDA and high K+.
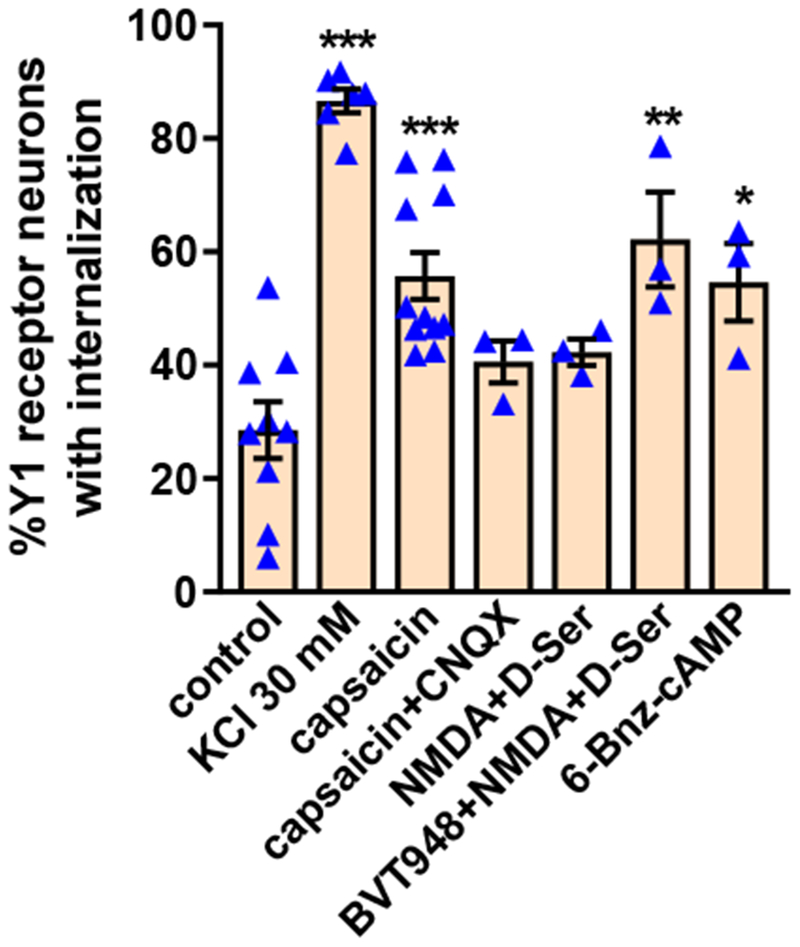
Rat spinal cord slices were untreated (control) or incubated at 35 °C as follows: 2 min in aCSF containing 30 mM KCl and 8 min in aCSF (KCl 30 mM); 10 min with 1 μM capsaicin (capsaicin); 10 min with 1 μM capsaicin and 10 μM CNQX (capsaicin + CNQX); 2 min with 10 μM NMDA and 10 μM D-serine and 8 min in aCSF (NMDA+D-Ser); 60 min with 10 μM BVT948 (protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor), 2 min with 10 μM NMDA + D-serine and 8 min in aCSF (BVT948+NMDA+D-Ser), or 60 min with 6-Bnz-cAMP 10 nM. Slices were fixed and the Y1 receptor antibody was used for immunofluorescence. Y1 receptor neurons were counted in laminae I and II. ANOVA, p<0.0001; Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: *** p<0.001, ** p<0.01 compared to control.
