Figure 7 -. Y1 receptor internalization induced by dorsal root stimulation.
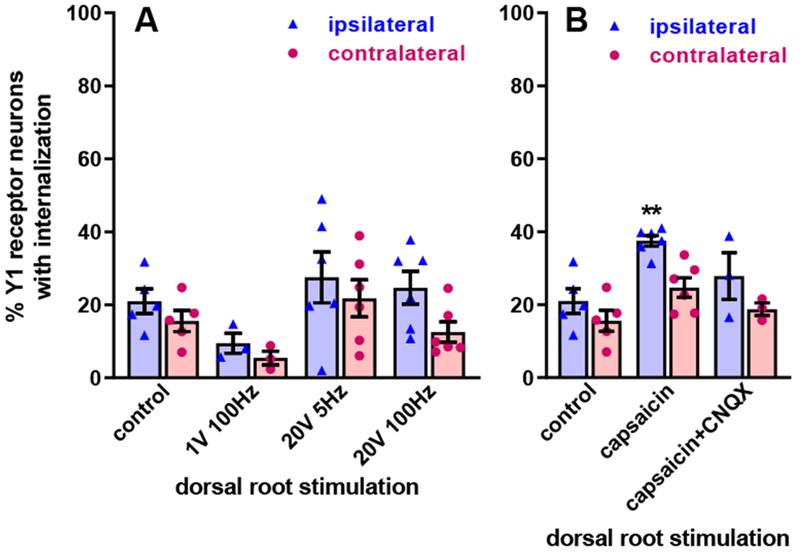
A. Electrical stimulation: one dorsal root contiguous with the spinal cord slice was put on a side chamber through a grease bridge, placed on a bipolar electrode and covered with mineral oil. Then the root was stimulated with 1000 pulses of 0.4 ms duration, 1 V or 20 V, delivered at 5 Hz or 100 Hz, as indicated. After the stimulation, slices were superfused in the chamber for 10 min. “Control” slices are the same in both panels and were superfused in the chamber for 10 min. Repeated measures 2-way ANOVA: stimulation p=0.14, side (ipsilateral vs. contralateral) p=0.0015, interaction p=0.36. B. “Capsaicin”: the dorsal root was put into the side chamber and covered with 1 μM capsaicin for 10 min. “Capsaicin + CNQX”: the dorsal root was covered with 1 μM capsaicin while the slice was superfused with 10 μM CNQX for 10 min. Repeated measures 2-way ANOVA: stimulation p=0.010, side p=0.0005, interaction p=0.23. Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: ** p<0.01, compared to control.
