Figure 8 -. Y1 receptor internalization in spinal cord slices after spared nerve injury.
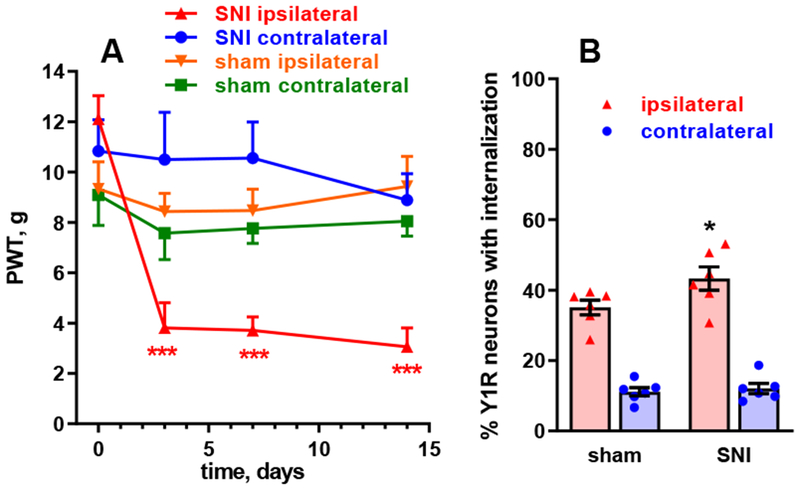
A. Rats received spared nerve injury (SNI) consisting in cutting the common peroneal and tibial nerves (n=6) or sham surgery (n=7). The development of mechanical hyperalgesia was followed for 14 days as responses to von Frey filament in the hind paws ipsilateral and contralateral to SNI. Repeated measures (by time and side) 3-way ANOVA yielded significant effects of time (p=0.0008) and side (p=0.0029), but not SNI (p=0.49), and significant interactions time x side (p=0.0044), time x SNI (p=0.0173), side x SNI (p=0.0002) and time x side x SNI (p=0.0006). Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: ***, p<0.0001 compared to baseline. B. On day 14, 3 spinal cord slices were obtained from each rat, which were stimulated at the ipsilateral dorsal horn with 1000 pulses of 20 V, 0.4 ms, delivered at 5 Hz. Y1R internalization was measured in sections from the slices. Repeated measures 2-way ANOVA yielded significant effects of side (p<0.0001) and interaction (p=0.0386), but not SNI (p=0.116). Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test: *, p=0.0289 compared with sham.
