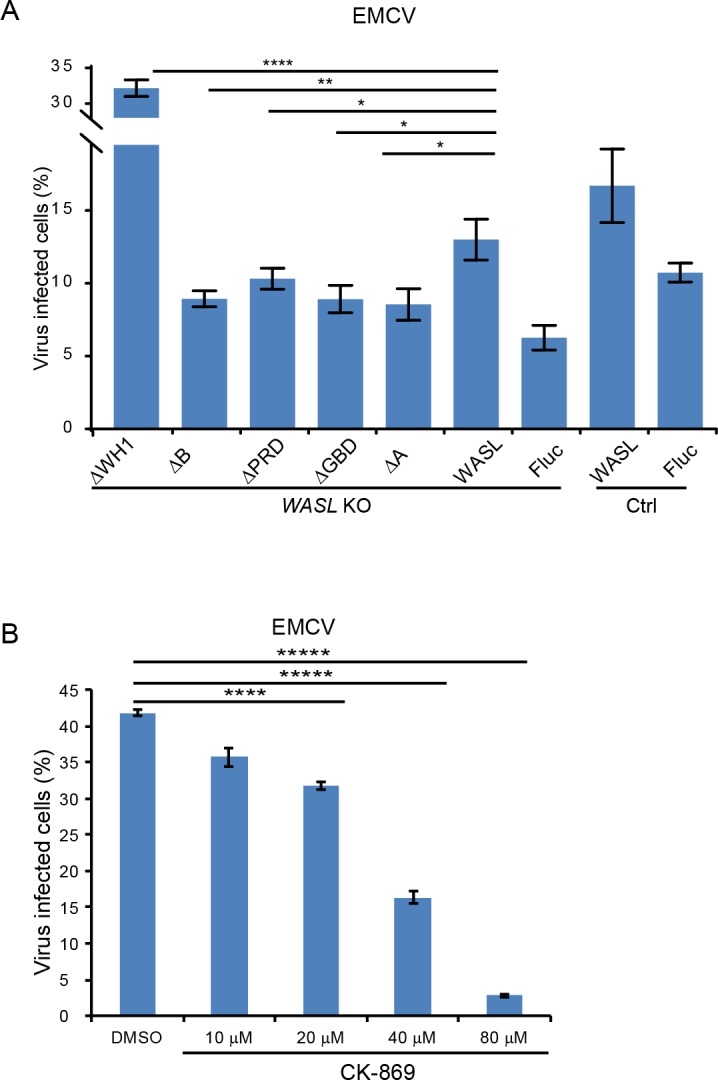
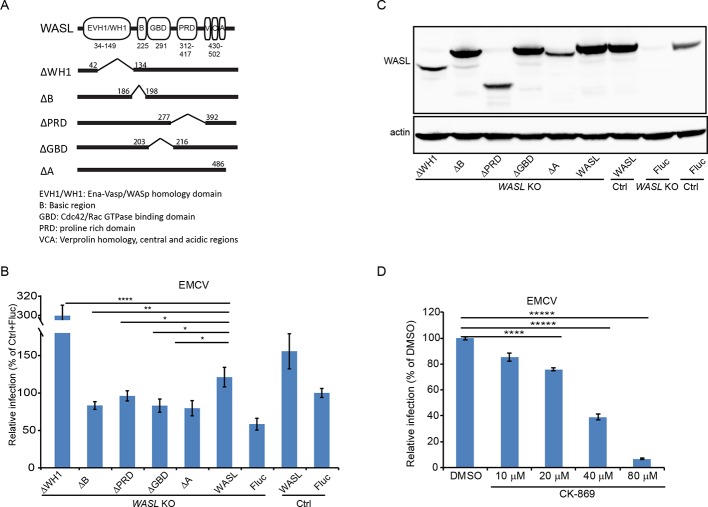
Figure 6. WASL activation and its actin modulation are critical for EMCV virus infection.
(A) Schematic representation of different WASL domain truncations. Each truncation is indicated by amino acid position on the constructs. (B) FACS quantification of EMCV infection in WASL KO cells transduced with different WASL domain truncations. (C) Western blot detection of WASL domain truncation expression constructs in lentivirus transduced WASL KO cells. (D) CK-869 inhibition of EMCV infection on naïve A549 cells at 10 hr post infection at an MOI of 1. (B, D) Error bars represent standard deviation of three replicates. The data shown are representative of two independent experiments. *: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, ***: p<0.001, ****: p<0.0001.
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. WASL activation and its actin modulation are critical for EMCV virus infection.