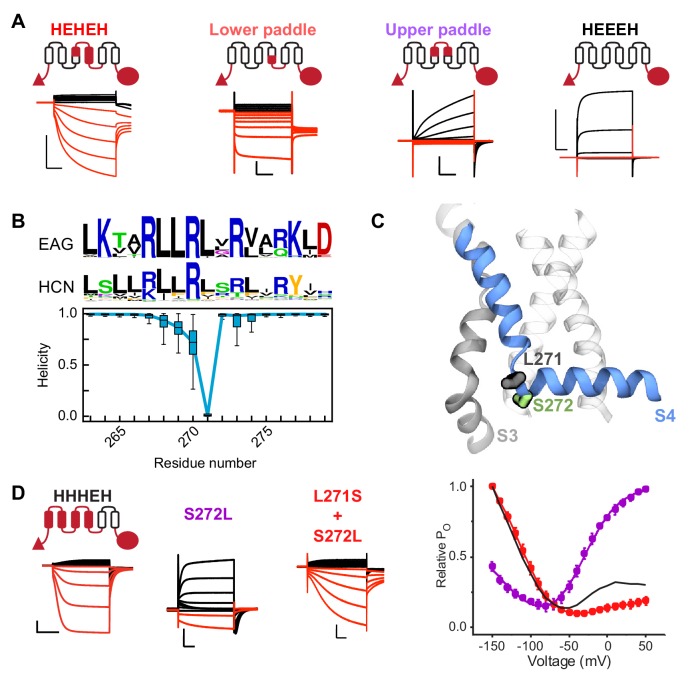
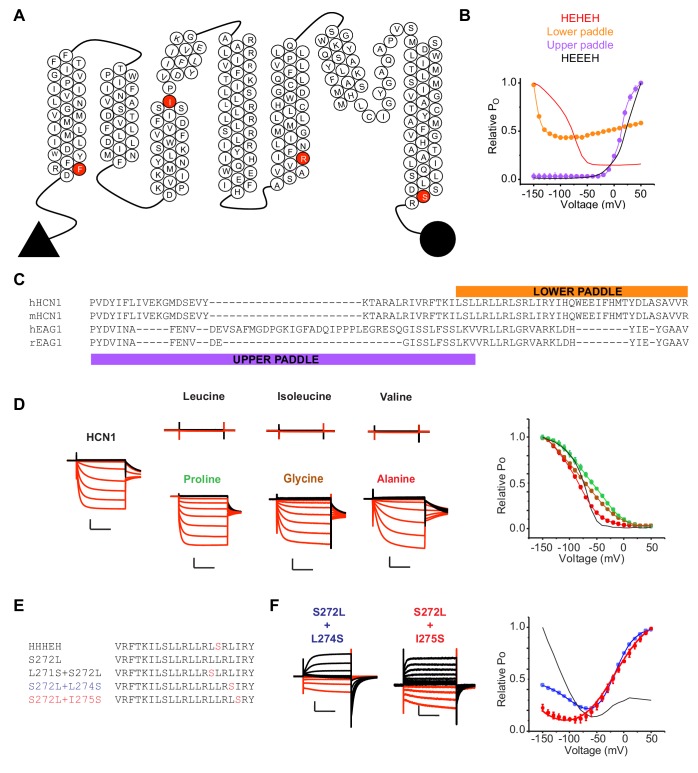
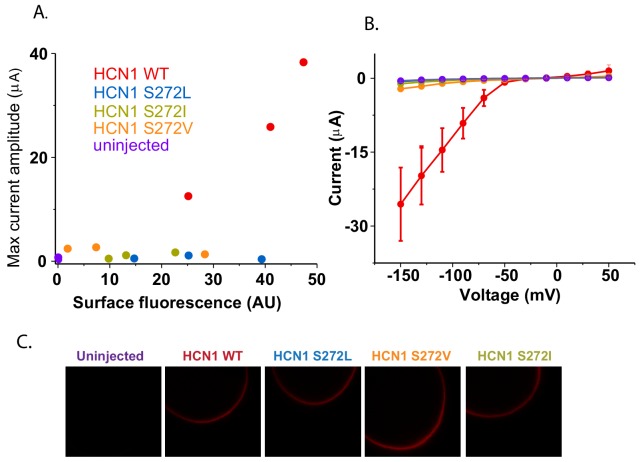
Figure 3. A conserved serine residue (S272) located in the lower half of the S4 segment is critical for hyperpolarization-dependent gating.
(A) Cartoon representations and representative current traces for chimeras with varying contributions of the HCN1 S4 helix. Black traces represent current responses to depolarizing pulses whereas are red ones depict current responses elicited by hyperpolarizing potential pulses. Test pulses range from −150 mV to 50 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV (lower paddle), −50 mV (HEHEH), or −90 mV (HEEEH and upper paddle). Scale bars show 5 µA (vertical) and 200 ms (horizontal). Color coding and scale bars are same throughout the figure. (B) Top: Consensus sequences from multiple sequence alignments for S4 helix of EAG and HCN families shown as sequence logos (Crooks et al., 2004). The height of each residue is proportional to its frequency, while the height of the overall stack of residues is inversely proportional to Shannon entropy. Bottom: Helicity of S4 helix plotted as a function of residue position in the activated state of HCN1 from simulations. The box plot shows the median, 25–75% (box), 1–99% (bars) of the data collected from the six voltage sensors that underwent activation. (C) Structure of a representative activated state model highlighting the position of key residues near the bend (L271 and S272 in gray and green sticks, respectively). (D) Left: Representative current traces from the bipolar chimera HHHEH and mutants of this background near the site of the S4 bending. Test pulses range from −150 mV to 50 mV from a holding potential of −50 mV (HHHEH and L271S+S272L) or −100 mV (S272L). Right: Relative PO vs. voltage curves for the mutants. Error bars represent standard deviation n = 4 (S272L), 4 (S271S+S272L) from independent measurement.