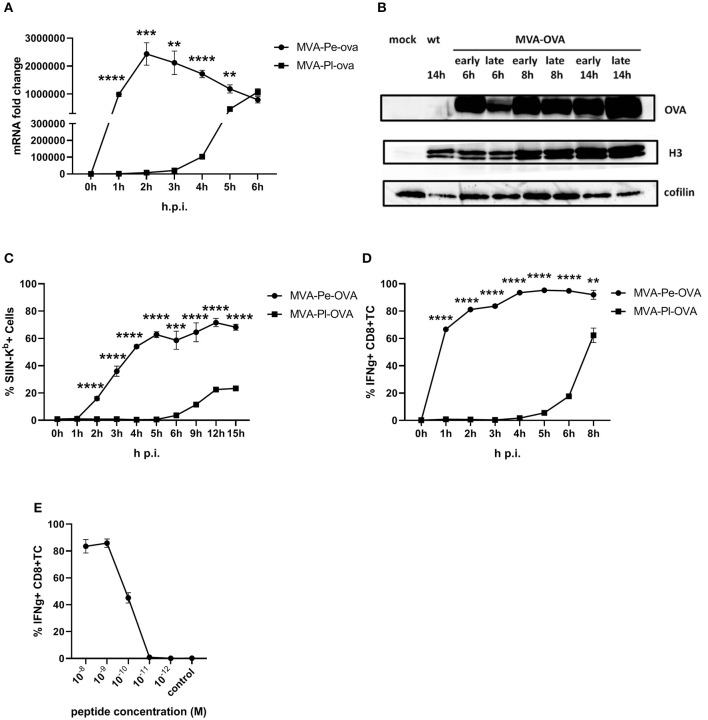
Figure 2.
Presentation of OVA to OVA257-CTL is significantly delayed and reduced when expressed as a late antigen. (A) The mRNA levels for OVA were determined by qRT-PCR in C57BL/6 BMDC infected with MVA-Pe-OVA or MVA-Pl-OVA with MOI 10 between 0 and 6 h p.i. (B) Western blot analysis for OVA protein synthesis in cell lysates from BMDC infected with MVA-Pe-OVA or MVA-Pl-OVA harvested at the indicated time pints p.i. Viral protein H3 served as an infection control, cellular cofilin as a loading control. Anti-OVA, anti-H3, and anti-cofilin antibodies were used. (C) Kinetic analysis of SIINFEKL/Kb complex expression at the surface of MVA-Pe-OVA or MVA-Pl-OVA infected BMDC. Mouse anti-SIINFEKL/Kb APC antibody was used after the viability dye staining. Frequency of SIINFEKL/Kb+ cells (% SIIN-Kb+ cells) is shown. (D) Activation of OVA257-CTL from C57BL/6 BMDC infected with MVA-Pe-OVA or MVA-Pl-OVA for the indicated hours. ICS (4 h) for IFNg production in OVA257-specific CD8+ T cells is shown. (E) Peptide titration showed valid avidity for OVA257-CTL. BMDC were loaded with indicated peptides at concentrations ranging from 10−8 to 10−12 M or with irrelevant MHC class I binding peptide (control) at 10−8 M as negative control. ICS for IFNg production. All data are means and SEM (n ≥ 3) from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Student's t-test).