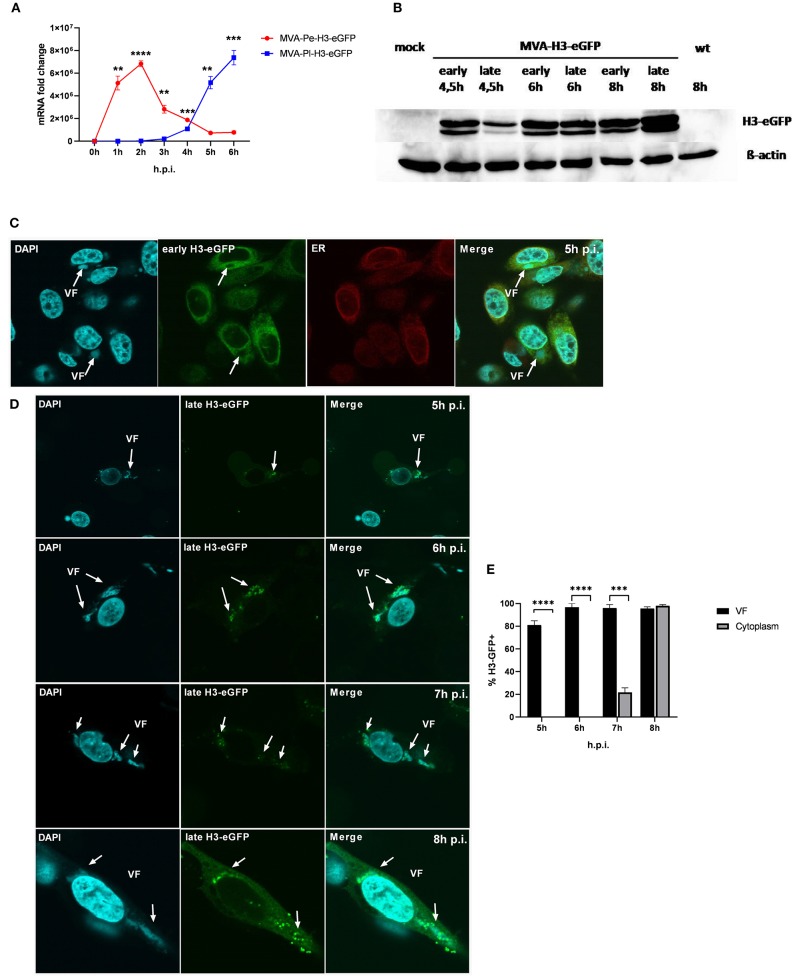
Figure 5.
Trapping of late viral proteins (H3-eGFP) in viral factories (VFs). (A) mRNA expression kinetics for H3-eGFP in BMDC infected with either MVA-Pe-H3-eGFP (early expression) or MVA-Pl-H3-eGFP (late expression) with MOI 10 determined for 0–6 h p.i. GFP-specific primers were used. Data represent relative expression levels and are displayed as means and SEM (n ≥ 3) of results from at least three independent experiments. (B) Western blot analysis for protein Synthesis of early and late expressed H3-eGFP. BMDC were infected with MVA-Pe-H3-eGFP (early) or Pl (late) for indicated hours at MOI 10. Mouse anti-GFP Ab was used to stain the H3-eGFP fusion protein. ß-actin was used as loading control. (C) Localization of H3-eGFP by CLSM. Early H3-eGFP (green) co-localized with ER at 5 h p.i. in HeLa cells infected with MVA-Pe-H3-eGFP. Nuclei and VFs (blue), ER (red), white arrows indicate VFs. (D) H3-eGFP produced late during infection (late H3-eGFP) was detected in VFs at 5 and 6 h p.i. and started to translocate from VFs to cytoplasm at 7 h p.i.. At 8 h p.i. late H3-eGFP was present in VFs and cytoplasm in all infected cells. Nuclei and VFs (blue). eGFP indicates late-H3 location. White arrows point to VFs. CLSM pictures are representative for one of three independent experiments. (E) Quantification and statistical analysis for the colocalization of late H3-GFP (% H3-GFP+) with VF (black) and/or cytoplasm (gray) in infected cells. Data are means and SEM (n ≥ 30) from three independent experiments, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (two-tailed Student's t-test).