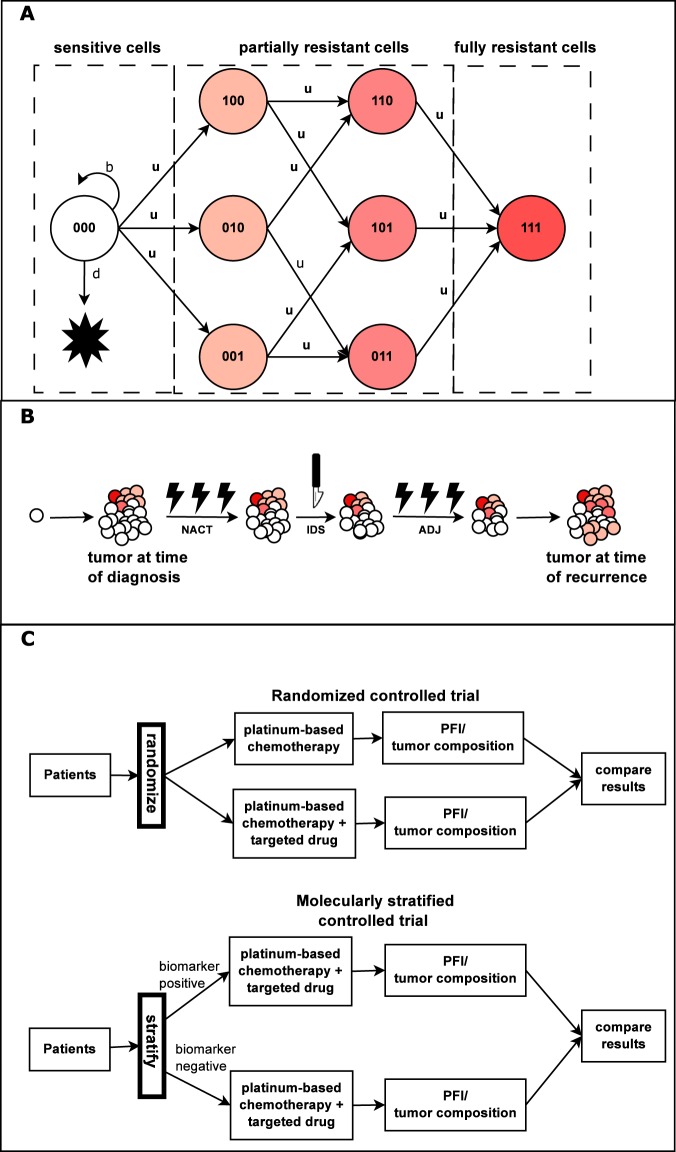
Figure 1.
Schematics of the mathematical model and virtual clinical trial simulations framework. Panel (A) We developed a mathematical model that consists of three main platinum resistance mechanisms, pre-target, on-target, and post-target resistance. Accordingly, this gives rise to eight types of cancer cells that are referred to as sensitive (no resistance mechanisms active), partially resistant (one or two resistance mechanisms active), and fully resistant (all three resistance mechanisms active). All cancer cells proliferate at rate b and die at rate d (only shown for sensitive cells). Panel (B) The model simulation starts from a single sensitive cancer and the tumor progresses until diagnosis (pre-treatment phase). We modeled HGSOC patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) standard-of-care (SOC) treatment for HGSOC, which consists of NACT followed by interval debulking surgery (IDS) and adjuvant chemotherapy (ADJ). After the treatment phase, the model is simulated until the first recurrence (post-treatment phase. Panel (C). The simulations contain randomized controlled trial simulations (RCTSs) and molecularly stratified controlled trial simulations (MSCTSs). An RCTS estimates the added value of a drug in a general HGSOC patient cohort and corresponds to traditional clinical trials where patients are not stratified based on a molecular biomarker. An MSCTS estimates the added value of using a molecular biomarker that stratifies patients according to their dominant drug resistance mechanism.