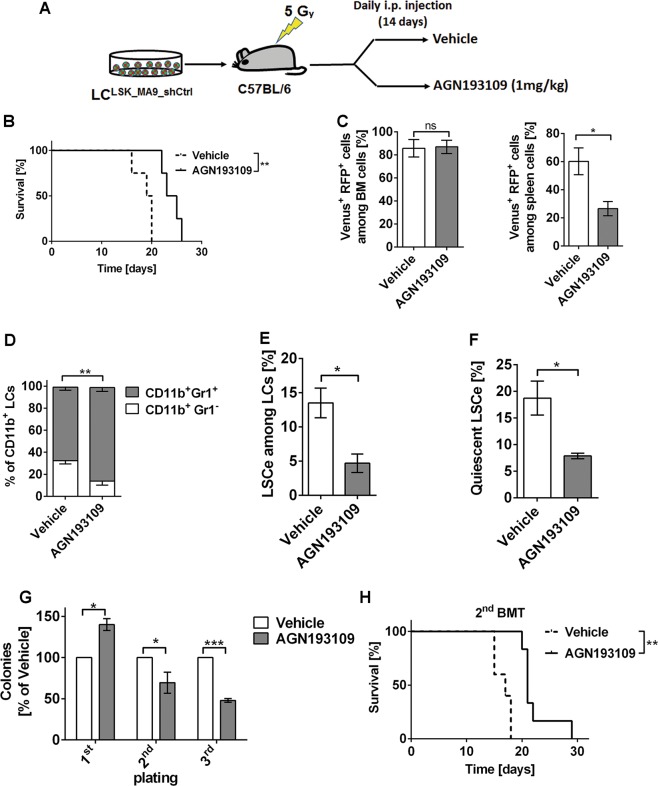
Fig. 6. The pan-RAR antagonist AGN193109 delays leukemogenesis and decreases stemness in MA9-driven, Evi1high murine AML.
a Schematic of experimental design. b Kaplan–Meier plot of mice transplanted with LCLSK_MA9_shCtrl (40,000 cells/mouse) and treated with AGN193109 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle (2.55% DMSO in PBS) by daily intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection for 14 days. n = 4/group; **p < 0.01; log-rank test. c–f Flow cytometric analysis of spleen (c) and BM cells (c–f) derived from terminally ill, AGN193109 or vehicle treated mice. LCs were defined as Venus+ RFP+ cells, but similar results were obtained if the analyses were not restricted to shCtrl expressing cells, but included all leukemic (Venus+) cells. n = 4; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns, not significant; t-test. c Percentages of LCs among BM and spleen cells. d Myeloid differentiation. e Proportions of LSCe among LCs. f Proportions of quiescent LSCe (LSCe in G0). g Colony formation in methyl cellulose by LCs, presented as percent of colonies from vehicle-treated mice in each round of plating. n = 3; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-hoc test. h Kaplan–Meier plot of mice transplanted with BM LCs derived from terminally ill, AGN193109 or vehicle treated mice (20,000 cells/mouse). n = 5/group; **p < 0.01; log-rank test. 2nd BMT, secondary bone marrow transplantation.