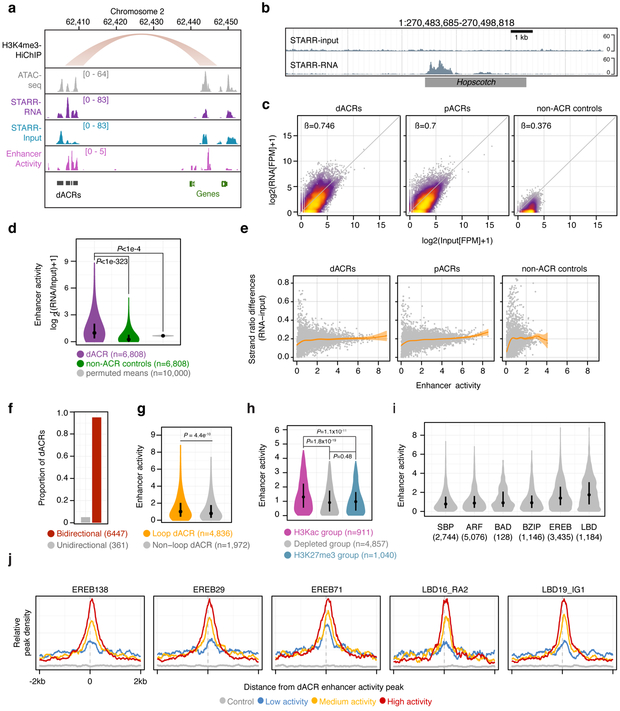
Fig. 5 ∣. Distal ACRs display elevated transcriptional enhancer capacity.
a, representative region showing a H3K4me3-HiChIP loop, ATAC-seq, RNA from STARR-seq, input from STARR-seq, and the estimated enhancer activity using the log2-transformed ratio of STARR-seq signal to input (RNA/input). b, STARR DNA input from a bacterial artificial chromosome (top track) and its corresponding RNA output (bottom track) at the Hopscotch positive control locus characterized by Studer et al (2011). c, STARR-RNA versus STARR-input fragments per million (FPM) across distal ACRs (dACRs, including H3Kac, depleted, and H3K27me3 group dACRs and excluding transcribed group dACRs; left panel), proximal ACRs (pACRs, middle panel), and intergenic control regions (right panel). Regression coefficients are from a generalised linear model. d, Distributions of enhancer activities (max log2[RNA/input] FPM) for dACRs (excluding the transcribed group) and matched control regions compared (Mann-Whitney; two-sided; P<10−323), and mean enhancer activities of permuted random mappable regions matched in length to dACRs (n=6,808 regions per iteration, n=10,000 Monte Carlo iterations). e, Absolute difference in strand ratios between STARR-RNA and STARR-input fragments for dACRs (left), pACRs (middle), and control regions (right) relative to enhancer activity. f, Proportion of dACRs with bidirectional and unidirectional activity determined by a betabinomial model. The number of dACRs are shown in parenthesis. g, Distribution of enhancer activities for dACRs coincident or non-coincident with HiChIP loop edges (Mann-Whitney; P<4.5×10−10). h, distribution of enhancer activities among the different dACR chromatin group classifications. Hypothesis tests were performed using Mann-Whitney. i, Distribution of enhancer activities overlapping binding site peaks of DAP-seq-profiled TF families. n = the number of dACRs containing DAP-seq peaks. j, Average density of DAP-seq peaks centered on enhancer activity summits within dACRs. dACRs are split by enhancer activity. The sample sizes used for metaplots in j were the same as in i. The STARR-seq experiment described in this figure was performed as a single biological replicate. Boxplots shown in d, g, h, and i comprise medians (black dots) and quartiles. Violin plots depict 0-99% of the entire distribution.