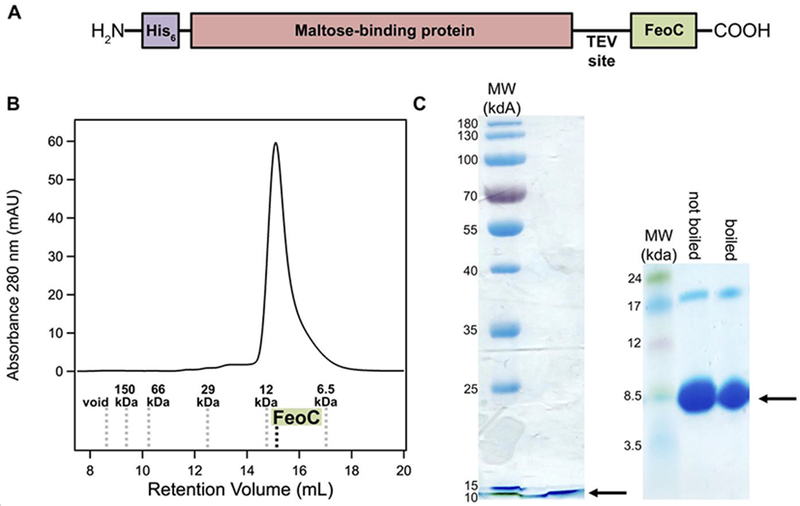
Figure 2.
Construct design and purification of EcFeoC. A. Because of poor native expression, EcFeoC was expressed as a maltose-binding protein (MBP; salmon) fusion (MBP-EcFeoC). On the N-terminus is encoded an additional (His)6 tag (purple) for orthogonal purification. Preceding the EcFeoC portion of the polypeptide (green) is an encoded TEV protease cleavage site. B. Cleaved, purified EcFeoC is monomeric (≈ 9000 g/mol, 9 kDa) based on its gel-filtration retention volume on Superdex 75. The compared standards (Kav versus log MW, linearity R2=0.97) are: blue dextran (void), alcohol dehydrogenase (150000 g/mol, 150 kDa), bovine serum albumin (66000 g/mol, 66 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29000 g/mol, 29 kDa), cytochrome c (12000 g/mol, 12 kDa), and aprotinin (6500 g/mol, 6.5 kDa). C. SDS-PAGE analysis (acrylamide mass fraction of 15 %, left panel) and Tris-tricine gel analysis (gradient of acrylamide mass fraction from 10 % to 20 %, right panel), demonstrating EcFeoC purity after cleavage and SEC. Black arrows indicate the location of the purified EcFeoC. A small amount of dimeric EcFeoC (≈ 18000 g/mol, 18 kDa) is observed in the Tris-tricine analysis at high protein concentration, but this dimeric species is only observed after freeze-thawing of the protein and cannot be dissociated by sample boiling.