Figure 2.
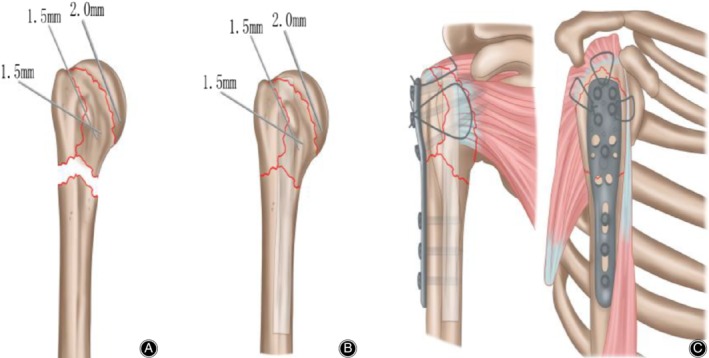
(A) (The illustration of the PHILOS combined with fibular allograft technology): A 2.0 mm Kirschner‐wire (K‐wire) was inserted into the humeral head to control rotation, and a periosteal elevator was used as a joystick at the fracture site to obtain reduction. After reduction of the greater tuberosity and humeral head, one or two 1.5 mm K‐wires were used for temporary fixation;(B) The allograft humerus is placed in the distal medullary cavity of the fracture, and the medial support is used to prevent the deformity and collapse of the humeral head in the long term; (C) Rotator cuff sutures were passed through the proximal humeral locking plate, and this was then slid from proximal to distal along the lateral aspect of the shaft, under the axillary nerve. The rotator cuff sutures were tied into place through eyelets on the plate, fixation was then obtained with screws and the wound was closed.
