Figure 1.
Identification of TTC29 Mutations in Five Unrelated Infertile Men and Functional Consequences of the c.176+1G>A TTC29 Variant
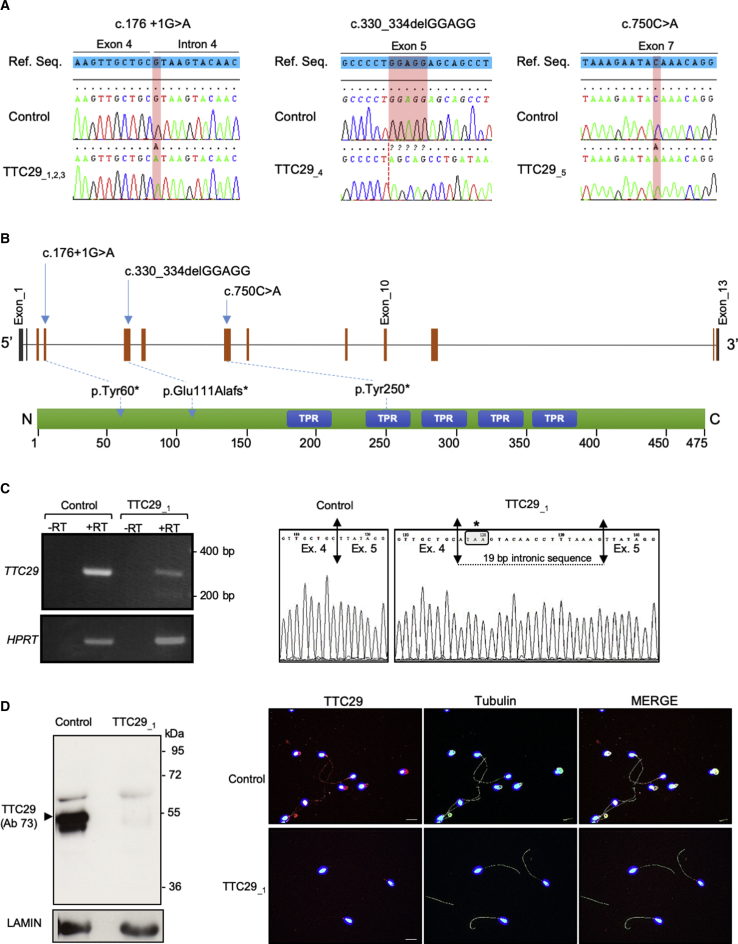
(A) Illustration of Sanger sequencing data for the TTC29 mutations identified in MMAF-affected infertile men: individuals TTC29_1, TTC29_2, and TTC29_3 carried the c.176+1G>A homozygous mutation; individual TTC29_4 carried the c.330_334delGGAGG homozygous mutation; individual TTC29_5 carried the c.750C>A homozygous mutation.
(B) Schematic representation of TTC29 exons structure (top) and predicted protein domains (bottom), according to SMART webtool and Uniprot, with position of the three different mutations identified in the gene. TTC29 encodes a protein of 475 amino acids that contains five tetratricopeptide domains (blue boxes).
(C) At the left, RT-PCR analysis on sperm sample from individual TTC29_1, carrying the c.176+1G>A mutation, which indicates a reduced amount of TTC29 transcript compared to control individual while HPRT transcript level was unaffected. At the right, electrophoregram of Sanger sequencing of the amplified transcript in sperm from individual TTC29_1, which shows an abnormal exon 4–5 boundary resulting in a premature stop codon, in comparison with control individual.
(D) Western blot and immunofluorescence analyses of sperm sample from individual TTC29_1, carrying the c.176+1G>A mutation, which both indicates the absence of TTC29 protein compared to control individual.