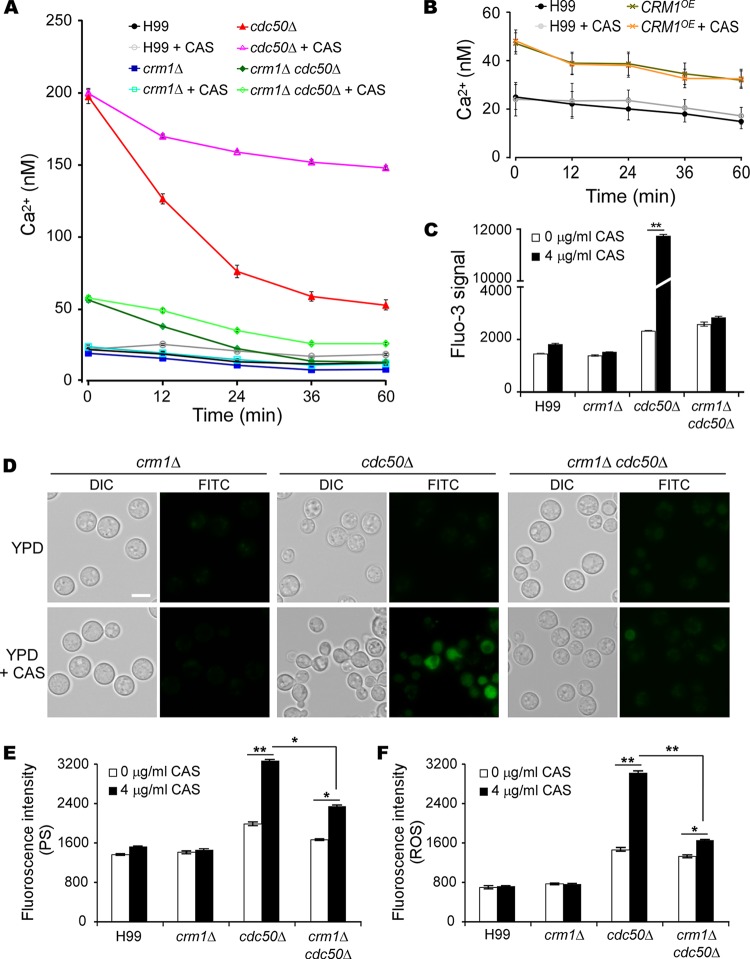
FIG 4.
Loss of Crm1 restores calcium homeostasis and decreases cell surface PS exposure and ROS production in the cdc50Δ mutant. Intracellular calcium levels, PS signal, and ROS signal were determined at the indicated time points by flow cytometry. Overnight cultures of the H99, cdc50Δ, crm1Δ, crm1Δ cdc50Δ and CRM1OE strains were resuspended in YPD containing 0 or 4 μg/ml caspofungin. (A) Time-lapse measurement of intracellular calcium levels in the presence and absence of caspofungin (CAS). (B) Intracellular calcium levels in the CRM1OE strain. (C) Fluorescent signal intensities of intracellular calcium levels after 16 h of incubation in the presence or absence of caspofungin treatment. (D) The fluorescent signal of fungal cells was detected by fluorescence microscopy after annexin V binding. Bar, 10 μm. (E and F) Quantification of fluorescent signal intensities of cell surface PS and ROS, as indicated, using flow cytometry for 100,000 yeast cells. Triplicates were used for each measurement. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (two-tailed t test).