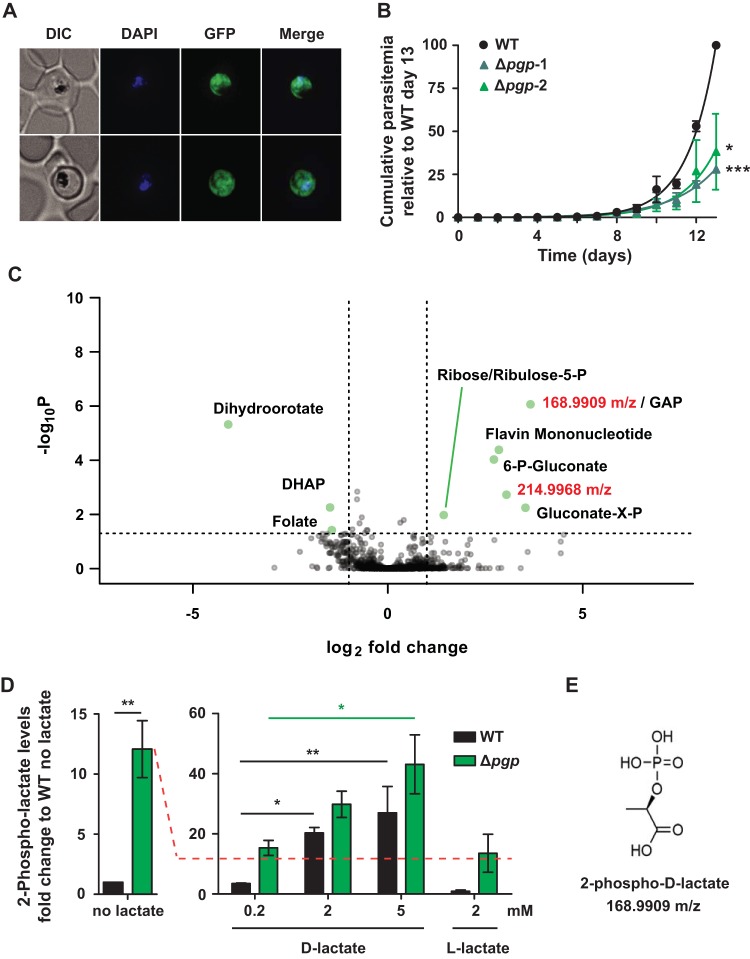
FIG 1.
PGP is required for normal growth of P. falciparum asexual stages, and Δpgp mutant parasites selectively accumulate metabolites in the PPP and two nonstandard metabolites. (A) Fluorescence microscopy of live PGP-GFP-infected RBCs. Infected RBCs were labeled with DAPI and visualized by differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence microscopy. GFP fluorescence was present throughout the cytoplasm. (B) The asexual growth of Δpgp strain- versus wild-type (WT)-infected RBCs was monitored daily over a 13-day period by flow cytometry following SYTO61 labeling. Data are presented as the mean ± standard errors of the mean (SEM) cumulative parasitemia normalized to the WT day 13 data point (100%) from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using a paired Student's t test at day 13 (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001). (C) Intracellular metabolite profiling of WT- and Δpgp mutant-infected RBCs by LC-MS. Individual metabolites are plotted as fold change (log2) versus –log10(P) for the Δpgp mutant parasites compared to WT parasites. Annotated metabolites were verified using standards, with the exception of gluconate-X-P (where the position of the P is unknown). Ribose-5-P and ribulose-5-P coelute under the chromatography conditions used. Two peaks of unknown identity, m/z 168.9909 and m/z 214.9968, also increased in the mutant line. (D) WT- and Δpgp mutant-infected RBCs were incubated with different concentrations of l- or d-lactate, and intracellular levels of 2-phospholactate were measured by GC-MS. Data are presented as fold change versus the WT (no lactate) condition. Data are presented as the means ± SEM from three independent experiments performed on different days. Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired Student's t test for the condition of WT with no lactate versus Δpgp mutant (**, P < 0.01), and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for all lactate stimulation conditions (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; all other comparisons were nonsignificant). (E) Structure of 2-phospho-d-lactate (C3H7O6P).