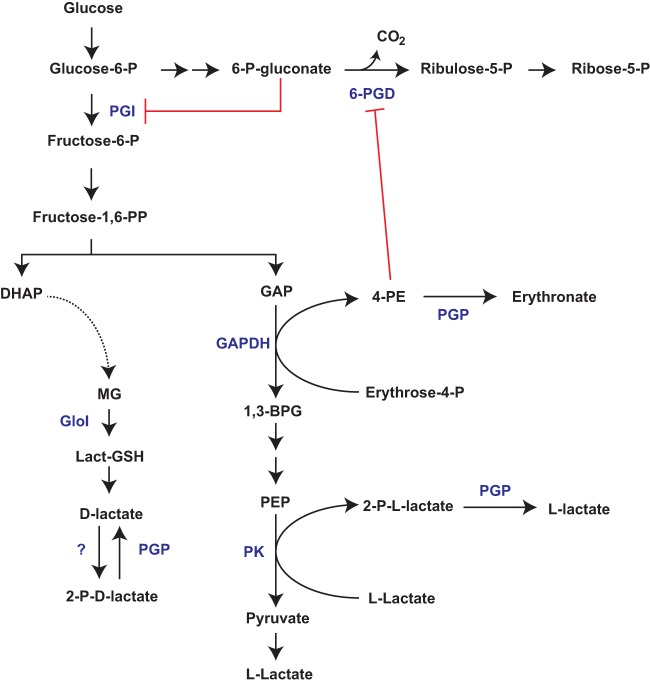
FIG 6.
PGP-mediated metabolite repair maintains flux through glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. PGP dephosphorylates 2-phospholactate (produced by an unspecified kinase[s] or a putative by-product of pyruvate kinase) and 4-phosphoerythronate (4-PE; a putative by-product of GAPDH). Loss of PGP leads to accumulation of 4-PE and partial inhibition of 6-PGD, with concomitant accumulation of 6-phosphogluconate and inhibition of enzymes in upper glycolysis. The PGP metabolic phenotype can be recapitulated by partial knockdown of 6-PGD. Abbreviations: glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (PGI), pyruvate kinase (PK), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6-PGD), glyoxylase I (GloI), phosphoglycolate phosphatase (PGP).