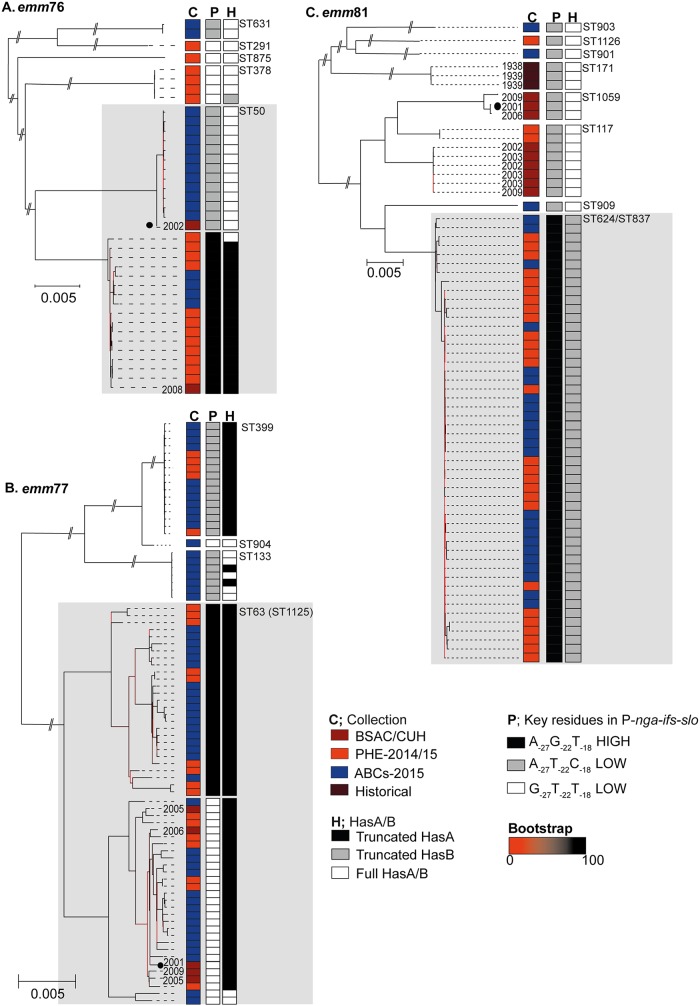
FIG 8.
Variants of P-nga-ifs-slo and capsule mutations associated with lineages of emm76, emm77, and emm81. Maximum likelihood phylogeny identified multiple sequence type (ST) lineages within the populations of emm76 (A), emm77 (B), and emm81 (C). Collection indicates either BSAC or CUH (dark red), PHE-2014/15 isolates (red), ABCs-2015 (blue), or English historical (brown). Dates for BSAC, CUH, or historical are shown; other isolates were from 2014/2015. STs are indicated on the right and major lineages are shaded gray. (A) Genome data for emm76 was mapped to the de novo assembled sequence of BSAC_bs448 from 2002, selected as the oldest isolate representing the genotype. Genome data from a total of 38 isolates were used: BSAC (n = 2), PHE-2014/15 (n = 18 [12, 13]), ABCs-2015 (n = 18 [14]). Predicted prophage regions were removed and a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree constructed from 30,264 core SNPs. Five STs were identified (indicated on right of tree), but the main lineage was ST50. (B) All emm77 genome data were mapped to the de novo assembled sequence of BSAC_bs150 from 2001. Genome data from a total of 80 isolates were used: BSAC (n = 5), PHE-2014/15 (n = 21 [12, 13]), and ABCs-2015 (n = 54 [14]). Four STs were identified but the main lineage was ST63, with one isolate in this lineage being single locus variant ST1125. Predicted prophage regions were removed, and a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed from 34,760 core SNPs. (C) All emm81 genome data were mapped to the de novo assembled seqeunce of BSAC_bs229 from 2001. Genome data from a total of 68 isolates were used: BSAC (n = 9), CUH (n = 1 [11]), PHE-2014/15 (n = 29 [12, 13]), ABCs-2015 (n = 26 [14]), and English historical 1930s (n = 3). Predicted prophage regions were removed, and a maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was constructed from 42,258 core SNPs. Nine STs were identified but the main lineage was ST624 with and minor (single base change in recP) ST variant ST837. We identified variants of P-nga-ifs-slo (P) associated with one of three combinations of key promoter residues, including the high-activity-associated A−27G−22T−18 (P; black). For emm76 (A) and emm77 (B), mutations were detected in hasA predicted to truncate HasA (H; black). (C) All emm81 isolates were predicted to express full-length HasA, but the ST624/ST837 lineage carried a mutation within hasB leading to a truncated HasB (H; gray). Branches are colored based on bootstrap support (scale bar provided). Scale bars represent substitutions per site. Isolates used as references for mapping indicated with black circles. Branches for lineages outside main lineages were shortened for presentation purposes (indicated by line breaks). C; collection, P; promoter key residue combination, H; full-length or truncated HasA or HasB.