Figure 7.
Mutations in Amino Sugar Metabolism Disrupt Liver-Stage Development
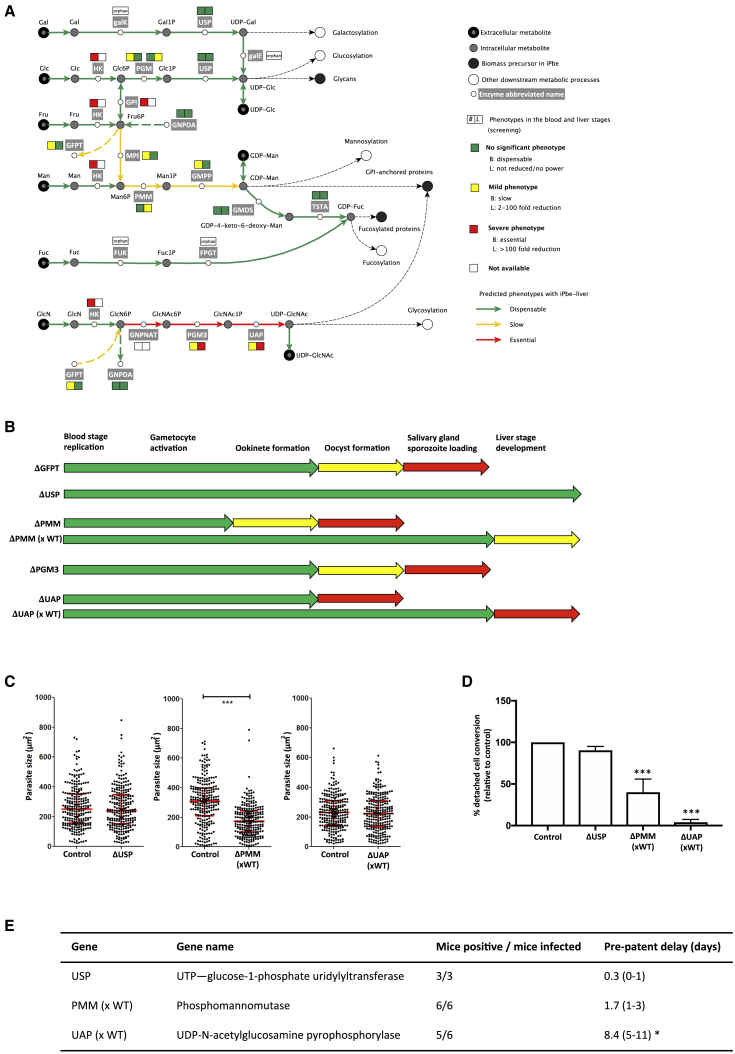
(A) Activation of sugars in the Plasmodium cytosol based on iPbe. See Table S4 for gene IDs, enzyme functions, and reactions. Gal, D-galactose; Gal1P, D-galactose 1-phosphate; UDP-Gal, UDP-d-galactose; Glc, D-glucose; Glc6P, D-glucose 6-phosphate; Glc1P, D-glucose 1-phosphate; UPD-Glc, UDP-glucose; Fru, D-fructose; Fru6P, D-fructose 6-phosphate; Man, D-mannose; Man6P, D-mannose 6-phosphate; Man1P, D-mannose 1-phosphate; GDP-Man, GDP-mannose; GDP-4-keto-6-deoxy-Man, GDP-4-dehydro-6-deoxy-d-mannose; GDP-Fuc, GDP-L-fucose; Fuc, 6-deoxy-L-galactose/fucose; Fuc1P, L-fucose 1-phosphate; GlcN, D-glucosamine; GlcN6P, D-glucosamine 6-phosphate; GlcNAc6P, N-acetyl-d-glucosamine 6-phosphate; GlcNAc1P, N-acetyl-alpha-d-glucosamine 1-phosphate; UDP-GlcNAc, UDP-N-acetyl-d-glucosamine.
(B) Schematic representation of developmental phenotypes of single KOs and mutants from ΔPMM × WT and ΔUAP × WT genetic crosses. Green, phenotype not significantly different from WT. Yellow, significantly reduced. Red, developmental block, except for liver stage, where red indicates phenotype significantly different from WT (>2-day delay in pre-patent period).
(C) Size of 250 cultured EEFs 48 hpi; median and interquartile ranges in red. ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗p < 0.05 by Kruskal-Wallis test.
(D) Relative maturation of EEFs measured as conversion of infected host cells to detached cells at 48 hpi. Error bars show standard deviations from 8 biological replicates. The results were statistically evaluated by a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test with Dunnet’s multiple comparisons (∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001).
(E) Overall transmission success given as the number of mice that became blood stage positive after injection of 5,000 sporozoites and the mean delay (range) in pre-patency compared to mice infected with WT. ∗, gene KO parasites with a significantly “slow” blood stage phenotype (Bushell et al., 2017). See Figure S6C for plots showing the course of blood stage infections after sporozoite injection.
Supplemental Information