Figure 3. Eaf3 Is Required for the Proper Cotranscriptional Recruitment of Prp45.
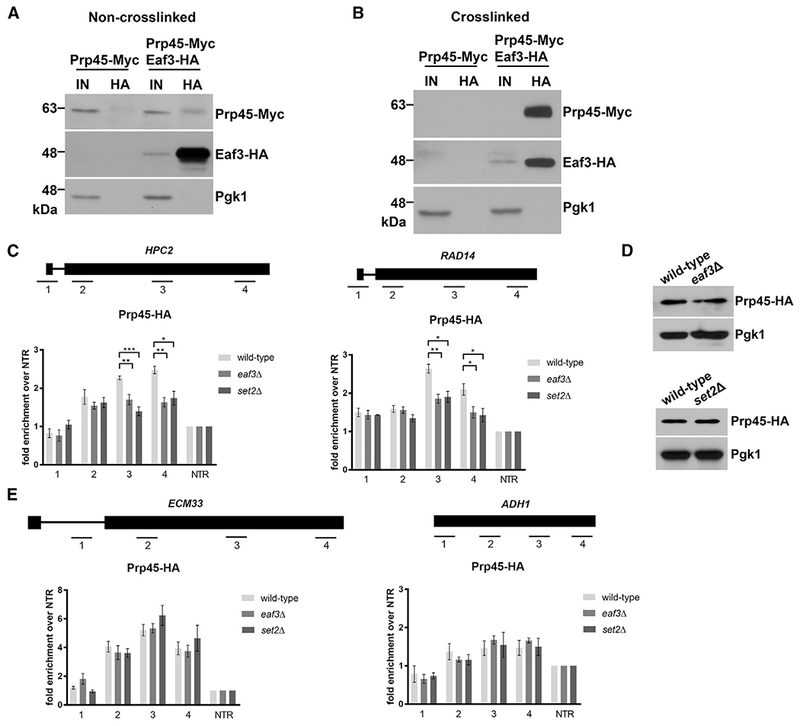
(A) Non-crosslinked co-immunoprecipitation (coIP) of Eaf3-HA and Prp45-Myc. Eaf3-HA was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. Input is 2% of total lysate used for pull-down. Products were analyzed by western blotting with an anti-HA antibody and anti-Myc antibody.
(B) Crosslinked coIP of Eaf3-HA and Prp45-Myc. Whole cell extracts were crosslinked with 1% for maldehyde. Eaf3-HA was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. Input is 2% of total lysate used for pull-down. Products were analyzed by western blotting with an anti-HA antibody and anti-Myc antibody.
(C) Occupancy of Prp45-HA on ICGs HPC2 (left) and RAD14 (right) relative to a non-transcribed region (NTR) on Chr. V in wild-type (light gray bars), eaf3Δ (medium gray bars), and set2Δ (dark gray bars).
(D) Western blot analysis of Prp45-HA protein levels in wild-type and eaf3Δ (top), and set2Δ (bottom) cells. Pgk1 is a loading control.
(E) Occupancy of Prp45-HA on ICG ECM33 and intronless gene ADH1 relative to a NTR on Chr. V. in wild-type, eaf3Δ, and set2Δ. Bars represent the average of at least 3 biological replicates. Error bars represent the SEM. p values were determined by 2-tailed unpaired t test. *, p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001.
