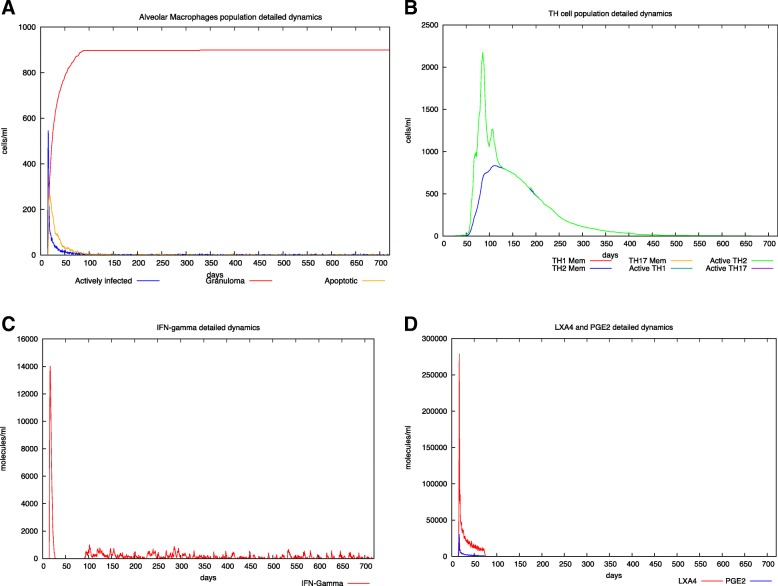
Fig. 2.
In silico latent tuberculosis infection scenario. Panel A depicts AM population dynamics. In particular, it is simulated the time course of the MTB-alveolar macrophages infected levels, the apoptotic ones and those forming granuloma. One can appreciate the typical granuloma behavior in LTBI as a potential protective immune system instrument from one side and the MTB reservoir of infection from the other one. Panel B shows Helper T cells dynamics. Subtypes (TH-1, TH-2 and TH- 17) are reported. LTBI induces a TH-2 switch instead of TH-1. This leads to a lesser immune system activation that could overcome the MTB spread. Panel C describes IFN-γ dynamics. After the first spike (representing the initial inflammatory response soon after the MTB infection), IFN-γ levels are kept almost at low level, indicating a latent typical scenario of immune system tolerance. In panel D LXA4 and PGE2 detailed dynamics are reported. The simulator correctly predicts a predominant LXA4 level indicating a pro-necrotic induction commonly observed in virulent strain of MTB causing a LTBI scenario. For all the simulated scenarios, time has been set to 720 days (2 years) and the virtual patient has been challenged with MTB at day 40