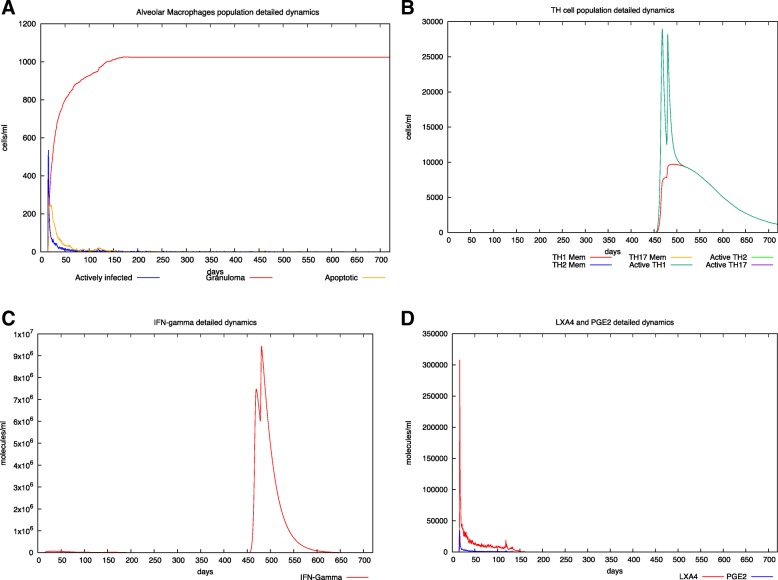
Fig. 4.
In silico latent tuberculosis infection with RUTI vaccine administration. Panel A depicts AM population dynamics. In particular, it is simulated the time course of the MTB-alveolar macrophages infected levels, the apoptotic ones and those forming granuloma. Panel B shows Helper T cells dynamics. Subtypes (TH-1, TH-2 and TH-17) are reported. The RUTI vaccine has been administered at day 450 and at day 478 (two inoculations, 28 days interval). CD4 T cells (TH-1 subtype) are the predominant one, indicating a strong immune system response induced by the therapeutical intervention. Panel C describes IFN-γ dynamics. Here one can appreciate the presence of two peaks of IFN-γ indicating the vaccine activity in stimulating pro-inflammatory and TH-1 mediated immune system response. Moreover, the level of IFN-γ dynamics prediction mirrors the one observed in the RUTI phase II clinical trial. In panel D LXA4 and PGE2 detailed dynamics are reported. The simulator correctly predicts a predominant peak of LXA4 indicating a pro-necrotic induction commonly observed in virulent strain of MTB. For all the simulated scenarios, time has been set to 720 days (2 years) and the virtual patient has been challenged with MTB at day 40