Fig. 12.
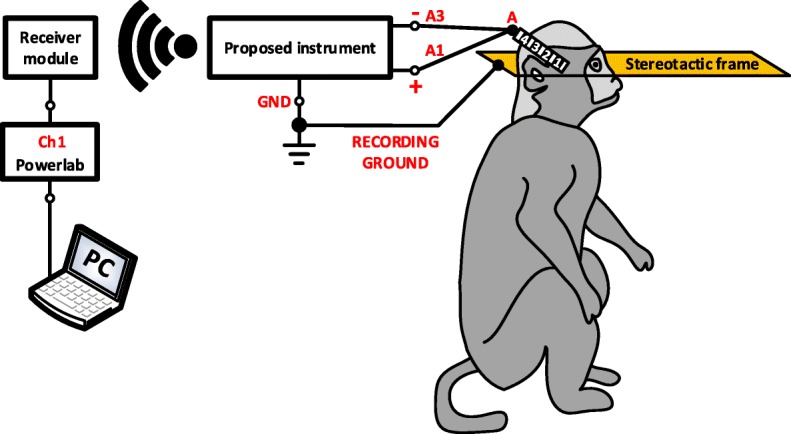
Experimental setup for evaluating the recording capabilities of the proposed instrument in vivo. A DBS electrode (electrode A, model DB-2201, Boston Scientific Neuromodulation) was implanted into the thalamus of an anaesthetised non-human primate. LFP signals were differentially recorded through contacts 1 and 3 of electrode A. The non-human primate was under anaesthesia with the head held in a primate stereotactic frame, which was connected to the ground of the recording system. The LFP signals were digitized by our instrument at a sampling frequency of 1 kSPS and were wirelessly transmitted to the receiver module (wireless transmission method – described in Fig. 8)
