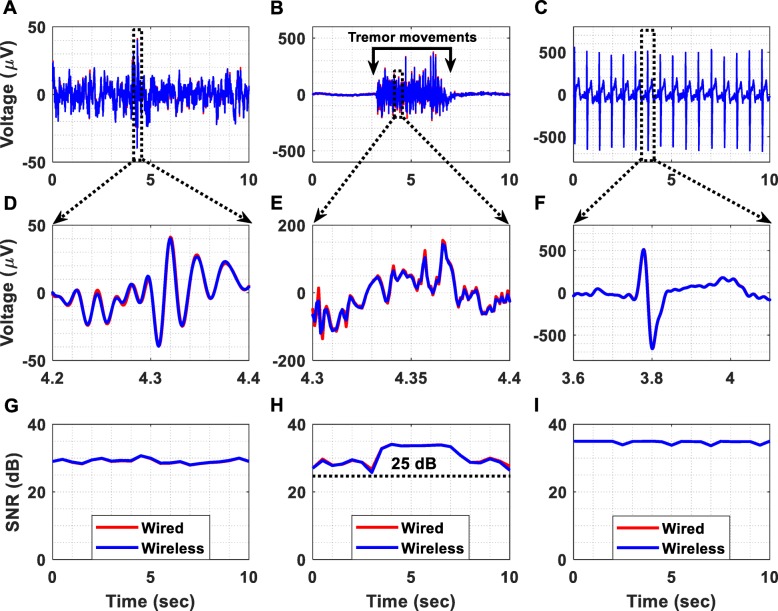
Fig. 9.
Biosignal acquisition using the setup presented in Fig. 8. The applied gain was 60 dB and the sampling frequency was equal to 1 kSPS. (a) Wired vs wireless EEG acquisition. (b) Wired vs wireless EMG acquisition from the palmaris longus muscle. (c) Wired vs wireless ECG acquisition. (d) Detailed view of the wireless and wired time-domain EEG recordings. (e) Detailed view of the wireless and wired time-domain EMG recordings. (f) Detailed view of the wireless and wired time-domain ECG recordings. (g) The SNR of the EEG signals was measured and found to be continuously higher than 25 dB. (h) The SNR of the EMG signals was measured and found to be continuously higher than 25 dB. (i) The SNR of the ECG signals was measured and found to be continuously higher than 30 dB