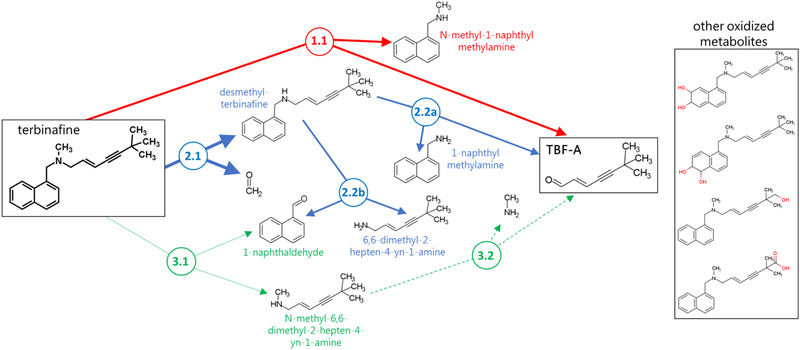
Fig. 1. N-Dealkylation pathways of terbinafine leading to formation of reactive TBF-A.
Three N-dealkylation pathways for terbinafine yield TBF-A. Pathway 1 (red) is the dominant pathway and consists of a single reaction yielding TBF-A and N-methyl-1-naphthyl methylamine as a co-metabolite (Step 1.1). Pathway 2 (blue) is also a major pathway and is a two-step pathway yielding first desmethyl-terbinafine and formaldehyde via very efficient N-demethylation (Step 2.1), followed by less efficient generation of 1-naphthyl methylamine and TBF-A from desmethyl-terbinafine (Step 2.2a) and 1-naphthaldehyde through a competing reaction (Step 2.2b). Pathway 3 (green) has minor significance and is a two-step pathway first yielding naphthaldehyde and N-methyl-6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-yn-1-amine (Step 3.1), which undergoes N-dealkylation to yield TBF-A (Step 3.2).