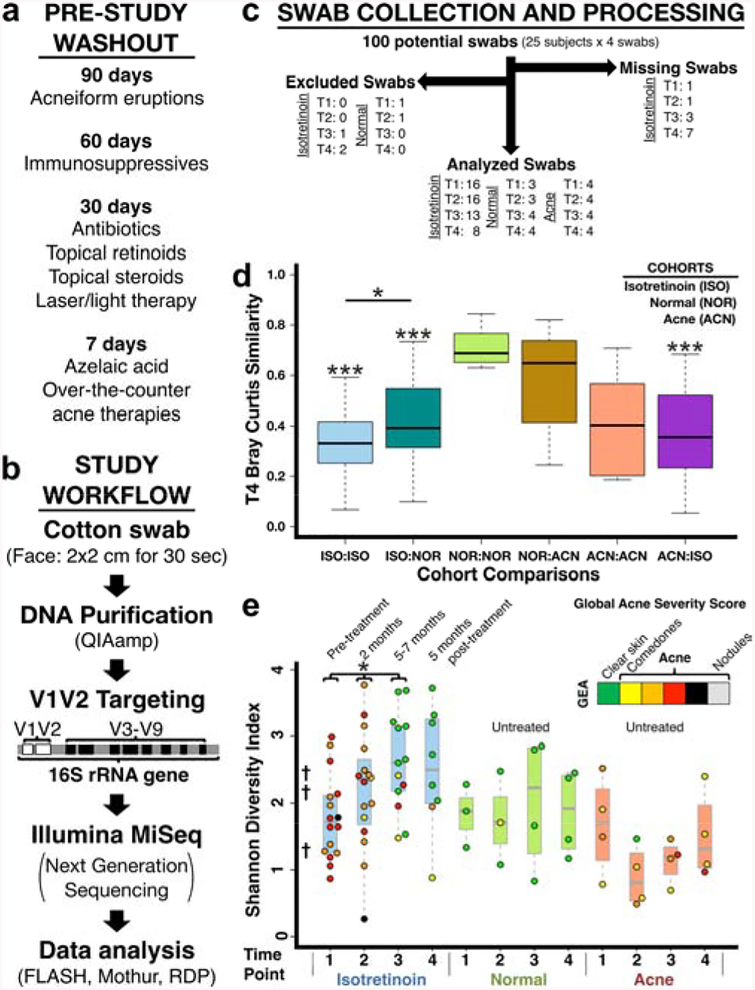
Figure 1. Study design, workflow, processing, and comparison to prior studies.
(a) Prohibited exposures listed by washout time. “Acneiform eruptions” refers to any medication/exposure reported to cause this presentation. (b) Study workflow from swab collection to genomic analysis. DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank Accession KCKB01000000. (c) Flow diagram of study swabs. Missing Swabs: not available due to subjects missing visits. Excluded Swabs (low quality swabs): poor 16S amplification (<5 ng/μl by qPCR) and/or low classified 16S sequence count (<2500). Swab numbers are listed by cohort and time point. (d) Post-treatment beta-diversity is significantly increased (i.e. decreased similarity) for isotretinoin subjects. (e) Alpha-diversity increases during treatment, remains elevated, and parallels the changing skin environment due to isotretinoin (sebaceous to dry). †Average Shannon diversity of prior Human Microbiome Project (HMP) study (Grice – sebaceous: 1.2, wet: 2.2, dry: 2.3). Data colored by acne severity (GEA). p-value<*0.05,***<0.001.