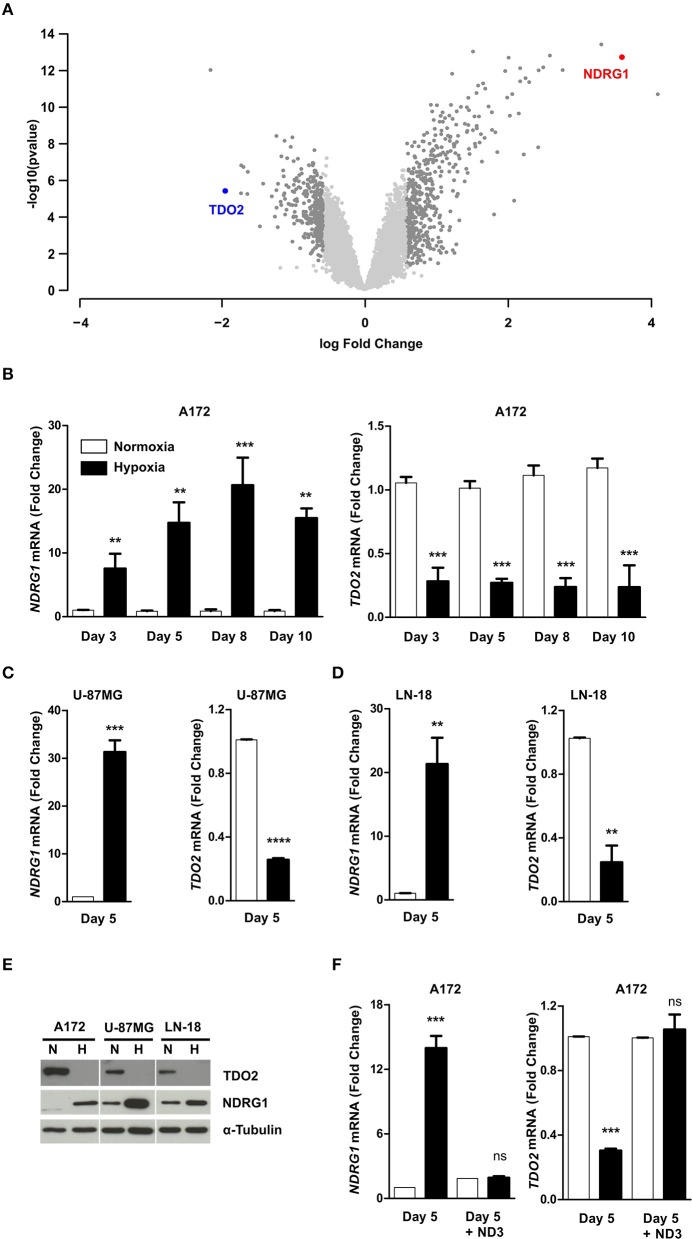
Figure 1.
Hypoxia reversibly downregulates tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO2) expression in GBM cells. (A) Volcano plot showing differentially regulated genes in A172 cells upon exposure to 5 days of hypoxia compared to 5 days normoxic controls. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of NDRG1 (left) and TDO2 (right) mRNA expression in A172 cells after 3, 5, 8, or 10 days of exposure to either normoxia (white) or hypoxia (back). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of NDRG1 (left) and TDO2 (right) mRNA expression in U-87MG cells after 5 days of either normoxia (white) or hypoxia (black) exposure. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of NDRG1 (left) and TDO2 (right) mRNA expression in LN-18 cells after 5 days of either normoxia or hypoxia. (E) Western blot analysis of TDO2 and NDRG1 protein expression in A172, U-87MG, and LN-18 cells subsequent to 5 days normoxia or hypoxia. α-Tubulin protein expression was used as a loading control. (F) NDRG1 (left) and TDO2 (right) mRNA expression in A172 cells analyzed by qRT-PCR after exposure to hypoxia for 5 days followed by re-oxygenation for 3 days under normoxic conditions (ND3). Data from at least three independent experiments are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was assumed at p < 0.05 (**p < 0.01, ***p <0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001). n.s., not significant.