Fig. 5. Relation of cognition to microglial gene expression and sleep fragmentation in participants with and without AD pathology.
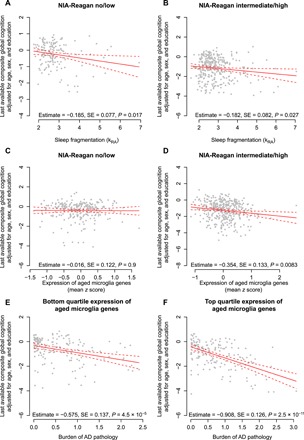
Partial residual plots of composite global cognitive summary score as a function of average antemortem sleep fragmentation (A and B) or the composite expression of genes enriched in aged microglia (HuMi_Aged_Old) (C and D) adjusted for age, sex, education, and methodological covariates. Each dot represents a single participant. Solid line represents the predicted cognition for an otherwise average participant. Dotted lines indicate 95% CIs on the prediction. Subjects with (A and C) low or no or (B and D) intermediate or high NIA-Reagan AD pathological classification. (E and F) Partial residual plot of composite global cognitive summary score as a function of the burden of AD pathology (composite of amyloid plaque and neurofibrillary tangle pathology) adjusted for age, sex, education, and methodological covariates. Subjects with (E) bottom quartile or (F) top quartile expression of genes characteristic of aged microglia. Each dot represents a single participant. Solid line represents the predicted cognition as a function of microglial gene expression for an otherwise average participant. Dotted lines indicate 95% CIs on the prediction.
