Fig. 5. PTPRE-AS1–deficient mice are more susceptible to CRE-induced asthma.
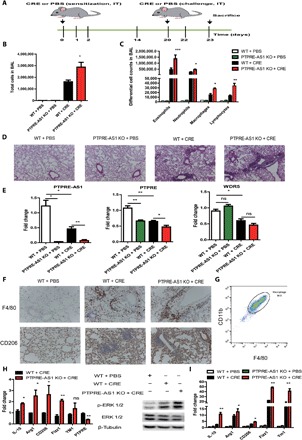
(A) Experimental CRE-induced asthma model including eight mice per group in each of the three independent experiments. (B) Total and (C) differential BALF cell numbers in PBS- and CRE-challenged PTPRE-AS1 KO and WT mice. (D) Representative images of H&E-stained lung tissues from PBS- and CRE-challenged PTPRE-AS1 KO and WT mice (magnification, ×100). (E) Levels of PTPRE-AS1, PTPRE, and WDR5 in lung tissues were detected by RT-qPCR. (F) Representative IHC images of F4/80 and CD206 expression in lung tissues (magnification, ×200). (G) The percentages of macrophages in purified cells from lung tissues were determined by flow cytometry. (H) The levels of M2-associated genes, PTPRE, and phosphorylated ERK 1/2 protein in IL-4–treated lung macrophages purified from experimental models were quantified. (I) RT-qPCR for M2-associated genes in lung tissue samples. The data shown were from one of three independent experiments. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
