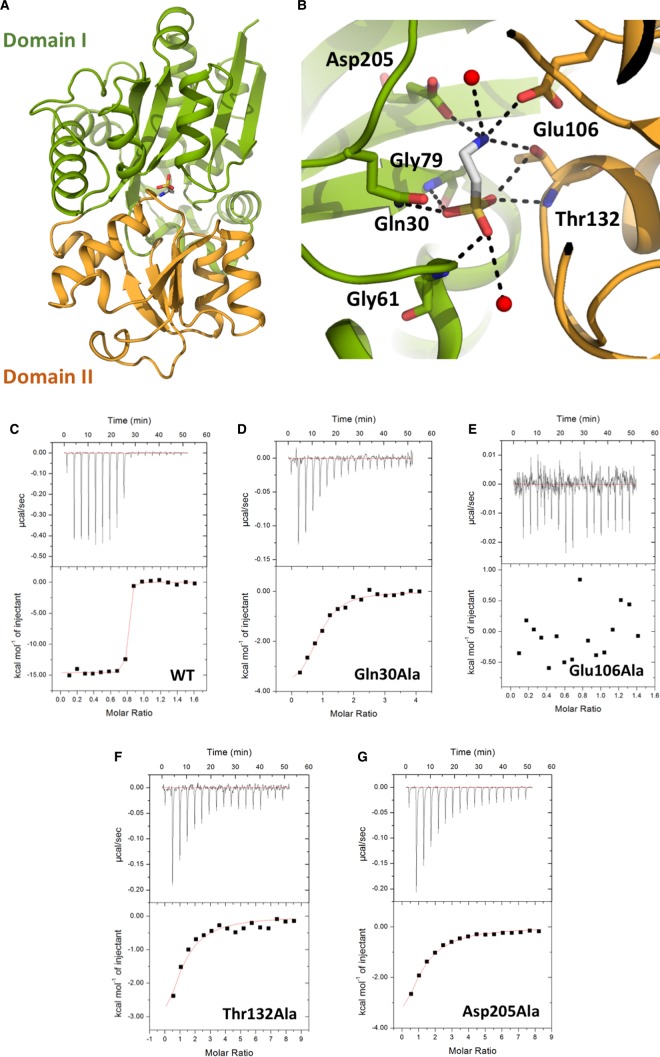
Figure 1. TauA crystal structure in complex with taurine and substrate binding site characterization.
(A) Cartoon representation of TauA in complex with taurine. Taurine is shown in sticks; carbon atoms are shown in gray, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue and sulfur in yellow. TauA displays a characteristic class II SBP structure with two globular domains, I and II, linked by a flexible linker; domain I is coloured green and domain II orange. Taurine binds in the cleft formed by the two domains. (B) Close-up view of the binding site. Taurine is bound by residues from both domains. Coordinating oxygens are shown as red spheres and hydrogen-bonds as dashed lines. Van der Waals interacting side chains have been omitted for clarity. (C–G) Calorimetric titration taurine binding to TauA and mutants (see also Table 1). Each peak (top panel) represents an injection of 2.4 µl of taurine into 200 µl of wild-type TauA or TauA mutant. The bottom panel shows the integrated heat obtained from the raw data, after subtracting the heat of dilution. Binding of taurine to TauA is exothermic with a binding affinity of 1.6 nM. All the TauA mutants show a decrease in taurine-binding affinity whereas the Glu106Ala mutation is detrimental to taurine binding.