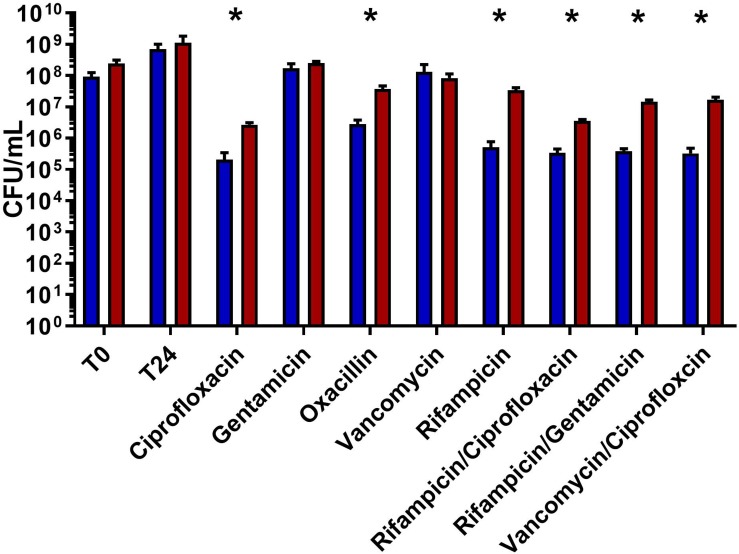
FIGURE 1.
Polymicrobial biofilms show increased tolerance to a variety of antibiotic. Overnight cultures of S. aureus were diluted 1:1000 and C. albicans overnight cultures were diluted 1:100 in TSB using a microtiter plate. Plates were incubated for 8 h at 37°C statically. Non-adherent cells washed, fresh media was added, and biofilms were subsequently challenged with antibiotics (10–100× MIC) for 24 h. S. aureus growing in polymicrobial biofilms (red) had significantly higher survival compared to biofilms only containing S. aureus (blue). Experiment was performed in biological triplicate and error bars represent standard deviation. Significance (as indicated by ∗) was determined using a t-test (p < 0.05).