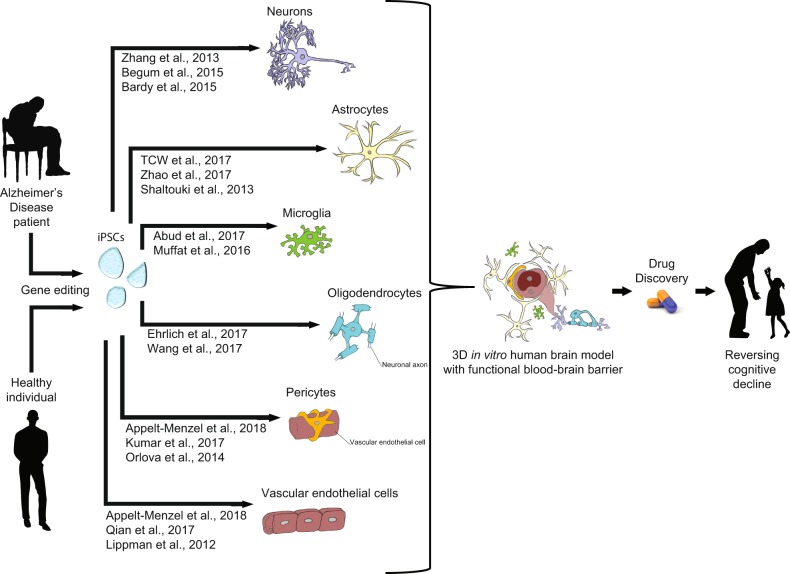
Fig. 2.
Human iPSC differentiation to brain cell types. Somatic cells from patients or healthy individuals can be reprogrammed to iPSCs and subsequently differentiated into all major brain cell types for in vitro studies. Such studies can examine cellular functions as well as how they are impacted by AD hallmark pathologies or AD-linked mutations. Genome editing techniques can be used to introduce or correct AD-linked mutations to examine phenotypes in isogenic backgrounds. 3D and co-culture models allow for examination of interactions occurring between cell types and sub-types to better model processes occurring in vivo. These and developing techniques hold promise for better understanding the relevant pathomechanisms underlying AD, and will hopefully facilitate development of effective therapeutics to combat dementia