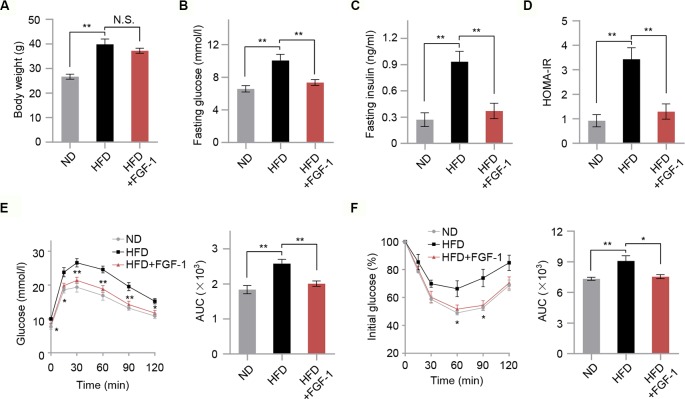
Figure 1.
Effects of FGF-1 on insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obesity (DIO) model mice. (A) The body weight in mice from ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 groups. Mice after subcutaneous injection of vehicle control (PBS) or FGF-1. n = 6 per group. (B–D) Overnight fasting serum glucose levels (B), insulin levels (C), and insulin resistance index HOMA-IR (D) measured from ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 groups. HFD-fed mice in response to chronic treatment with 0.1 mg/kg body weight FGF-1 every day (n = 6 mice per group). (E–F) Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT, n = 5 mice per group) (E) and insulin tolerance test (ITT, n = 6 mice per group) (F) of DIO mice after 8 weeks of FGF-1 treatment. Areas under the curve (AUC) for OGTT and ITT were calculated. DIO mice were injected subcutaneously with 0.1 mg/kg FGF-1 or PBS every day for 8 weeks. Error bars denote SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Tukey in (A–F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; N.S. not significant.