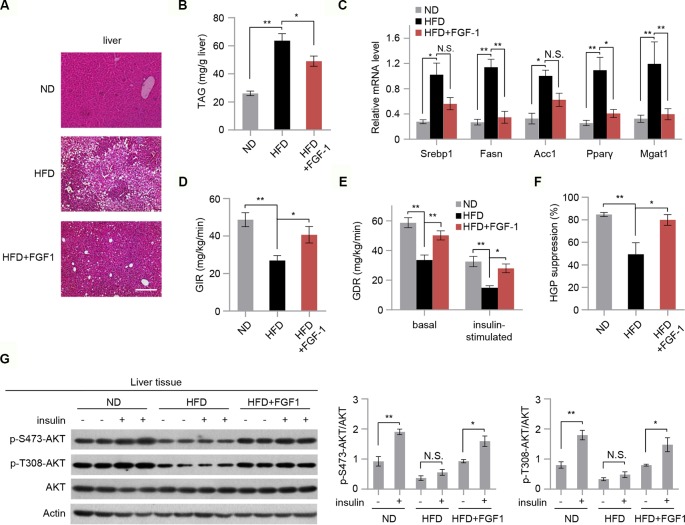
Figure 2.
FGF-1 attenuates HFD-induced hepatic steatosis and increases hepatic insulin sensitivity. (A) Representative sections of liver from ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 groups. DIO mice subcutaneously treated with PBS or FGF-1. Scale bar, 200 μm. (B) Levels of triacylglycerol (TAG) in liver tissues of ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 mice (n = 6). (C) Analysis of mRNA levels of transcription factors (i.e., Srebp1, Fasn, Acc1, PPARγ, Mgat1) in livers from ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 group (n = 6). (D–F) Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp study in DIO mice after 8 weeks of PBS (n = 6) or FGF-1 (n = 6) administration. Glucose infusion rate (GIR, D), glucose disposal rate (GDR, E), and percent suppression of HGP (F) are shown. (G) Western blot analysis and quantification of AKT phosphorylation in liver after intraperitoneal injection of insulin or saline in ND, HFD, and HFD+FGF-1 groups. All mice were fasted 6 h before insulin or saline injection. Error bars denote SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Tukey in (B–G). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; N.S. not significant. Uncropped blots can be found in Supplementary Figure 5 .