FIGURE 1.
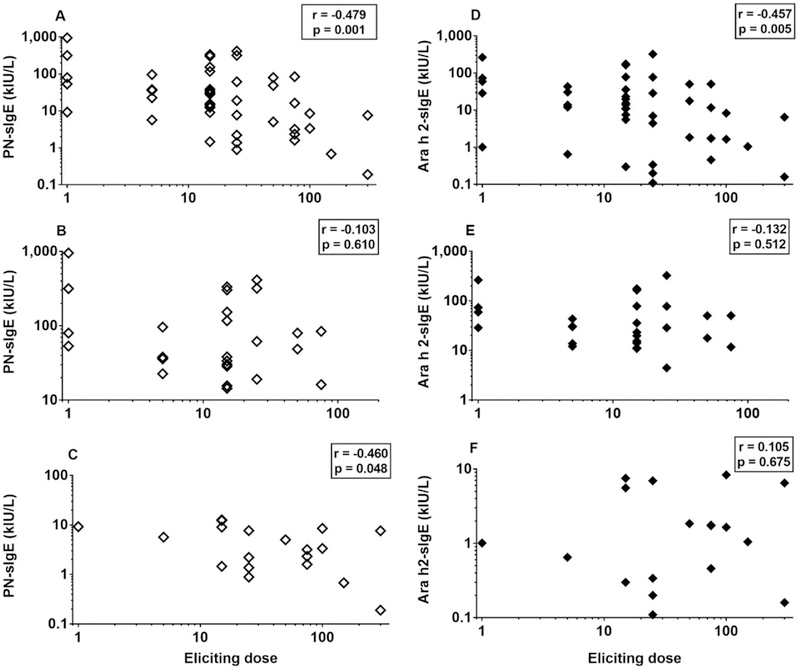
Increased levels of PN-sIgE are associated with lower eliciting dose upon oral challenge (A-C). This is true for the entire cohort (A) and for those with PN-sIgE < 14 kIU/L. However, this is not seen in those with PN-sIgE ≥ 14 kIU/L (C). Increased levels of Ara h 2-sIgE are also associated with lower eliciting dose upon oral challenge, but for the entire cohort (D). This relationship was not seen in the sub-groups with PN-sIgE < 14 kIU/L or with PN-sIgE ≥14 kIU/L (E, F). Data shown are for those who reacted to the initial challenge in the DEVIL study (n=46) (A, D) and for those who reacted and had PN-sIgE < 14 kIU/L (B, E) and those with PN-sIgE ≥ 14 kIU/L (C, F) (see Table E1).
