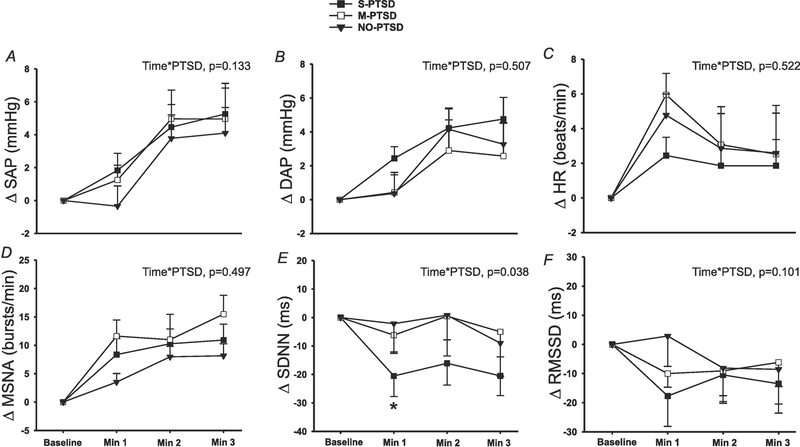
Figure 4:
Changes in systolic arterial pressure (SAP; panel A), diastolic arterial pressure (DAP; panel B), heart rate (HR; panel C), standard deviation of normal R-R intervals (SDNN; panel E) and root mean square of the successive differences (RMSSD; panel F) during 3 min of mental stress in 28 with severe posttraumatic stress disorder (S-PTSD) compared to 16 with moderate PTSD (M-PTSD) and 26 Controls (NO-PTSD). Change in muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA; panel D) in 26 S-PTSD compared to 13 M-PTSD and 22 Controls. SDNN reactivity to mental stress was significantly blunted in S-PTSD compared with M-PTSD and NO-PTSD. SAP, DAP, HR, MSNA and RMSSD reactivity to mental stress were not different between the groups. A linear mixed-model analysis was used to assess the within-group and between-group differences. *P < 0.05